The emergence of the novel coronavirus infection (COVID-19) in March 2020 led to a rapid increase in the number of countries affected. The World Health Organization (WHO, 2020a) declared the pandemic on 11 March 2020 due to the large number of infected people and the virus’s global spread. Preventive measures such as isolation and social distancing were adopted to avoid virus transmission in response to the health crisis. These measures have effectively reduced the number of cases and deaths but have also led to increased sedentary behavior and decreased regular physical activity (Márquez Arabia, 2020; Mera-Mamián et al., 2020). The sudden change in physical activity levels can hurt physical and mental health. For example, Bravo-Cucci et al. (2020) found that decreased physical activity during the COVID-19 pandemic was associated with an increased risk of obesity, cardiovascular disease, and depression.
According to Caspersen et al. (1985), physical activity encompasses any bodily movement resulting in energy expenditure, ranging from low to high levels. It’s a broad term closely related to physical exercise, physical aptitude, and sport. Physical exercise, specifically, involves planned, repetitive, and structured bodily movements aimed at improving physical fitness and strongly correlated with it. Distinguishing between physical activity and exercise isn’t always clear-cut, as there’s often overlap between the two (Biddle & Mutrie, 2008). Physical fitness, as defined by Caspersen et al. (1985), encompasses a range of attributes related to one’s ability to engage in physical activity. Some of these attributes are innate, while others are developed through individual levels of physical activity. Furthermore, sport refers to the competitive aspect of exercise governed by specific rules, characterized by strategic movements, skill, and chance. This study primarily focuses on physical activity in a general sense with measurements based on the definition provided by Caspersen et al. (1985).
The WHO (2020b) considers regular physical activity to benefit physical and mental health. It helps prevent and treat non-communicable diseases and contributes to general well-being by preventing cognitive impairment and symptoms of depression and anxiety. However, for physical activity to function as a protective factor, it must meet specific frequency, duration, intensity, type, and quantity criteria. In children and adolescents (ages 5-17), at least 60 minutes of activity per day, primarily aerobic, is recommended. Adults (ages 18-64) and older adults (ages 65 and older) should accumulate at least 75 minutes of vigorous or 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week. Evidence shows that women perform less physical exercise than men (Buckworth & Nigg, 2004; Darlow & Xu, 2011). This trend is repeated in Argentina, where men also exercise more than women (González Insua et al., 2020). 79.2% of the adults from the province of Buenos Aires reported engaging in some training before the pandemic (Herrera-Paz et al., 2020). However, only 9.2% reported more than 6 hours of training per week, 37.4% exercised less than 3 hours per week, and 20.7% did no physical activity during the quarantine.
Several studies have examined the association between physical activity and well-being during the COVID-19 pandemic. Well-being is a construct with various components, making it complex and controversial (Ryan & Deci, 2001). Historically, two main streams of well-being research can be distinguished, based on two different philosophies: the hedonic and the eudaimonic. The former reflects the idea that well-being consists of pleasure or happiness, with philosophical references such as Aristippus or Hobbes (Kahneman et al., 1999), while the latter argues that well-being lies in the realization of human potential, as represented by Aristotle or Fromm (Waterman, 1993). Regarding the hedonic tradition, although there are many ways to assess pleasure or displeasure in human experience, most research within this stream has used the concept of subjective well-being. It has three components: life satisfaction, presence of positive affect, and absence of negative affect (Ryan & Deci, 2001). Subjective well-being includes individuals’ judgments and evaluations of their own lives (Diener, 1984). These evaluations correspond to cognitive judgments and emotional responses to life in terms of a dichotomy between positive and pleasant emotions or negative and unpleasant emotions (Diener et al., 2018). The eudaimonic stream has a different view of well-being. It assumes that well-being is different from happiness per se, as proposed by the hedonic view, since not everything one expects to achieve or achieves contributes to well-being. Although these achievements may generate a sense of momentary pleasure, according to the hedonic view, some are not good for individuals and therefore do not lead to a state of well-being. In this sense, subjective happiness cannot be equated with well-being (Ryan & Deci, 2001). Waterman (1993) argues that while happiness is defined hedonically, the eudaimonic conception of well-being promotes living in accordance with one’s true self. Eudaimonia would then be generated by engaging in activities that align with deep values and entail a holistic and full commitment of the individual.
In Italy, Maugeri et al. (2020) found that reduced physical activity levels in the adult population were associated with lower psychological well-being. This association was particularly pronounced in women, suggesting that physical activity may play an essential role in women’s mental well-being during times of stress. Faulkner et al. (2020) surveyed adults in the United Kingdom, Ireland, New Zealand, and Australia within the first few weeks of COVID-19 restrictions. The results showed that people with positive exercise behaviors reported better mental health and well-being. A study of older adults in Spain (Carriedo et al., 2020) found that those who complied with WHO recommendations for vigorous-intensity physical activity and moderate-vigorous physical activity during quarantine had higher scores on resilience (locus of control, self-efficacy, and optimism), positive affect, and lower depressive symptoms. Jacob et al. (2020) investigated the association between physical activity levels and positive mental well-being, depressive symptoms, and anxiety symptoms in an adult sample of UK residents. The findings suggest that engaging in higher levels of physical activity during isolation is associated with better mental health.
The effects of green space physical activity and well-being have been explored in pre-pandemic contexts. Finlay et al. (2015) found that green and blue spaces impact older adults’ mental, physical, and social health. Rogerson et al. (2020) investigated the effectiveness of green exercise interventions in improving mental well-being, demonstrating that participants who initially reported low well-being could reach medium-high well-being. A comparison of outdoor and indoor exercise reveals that both have positive outcomes. However, exercising in natural spaces produces better results in psychological well-being, self-esteem, feelings of revitalization, energy, decreased tension, confusion, anger, and depression, and greater enjoyment and satisfaction with physical activity (Silva Piñeiro & Mayán Santos, 2016; Thompson Coon et al., 2011). Eigenschenk et al. (2019) conducted a systematic review of the benefits of outdoor sports. In terms of mental health and well-being, they found positive effects on general well-being, quality of life, happiness, and life satisfaction. They also described an increase in positive experiences and a reduction in negative affective states. This phenomenon can be explained by the stress reduction theory (Ulrich et al., 1991), which states that exposure to natural spaces elicits an unconscious response characterized by a decrease in physiological arousal, a decrease in negative affect, and an increase in positive affect.
Similarly, Marselle et al. (2014) investigated the effects of group nature walks on mental, social, and psychological well-being. They found that group nature walks are associated with higher positive affect and mental well-being and lower depression, perceived stress, and negative affect. These results suggest that engaging in group physical exercise contributes to most dimensions of psychological well-being in young athletes, particularly self-acceptance, environmental mastery, purpose in life, positive relationships with others, and general psychological well-being (Almeida et al., 2018; Kaplan, 1995; Lovell et al., 2016; Werneck et al., 2021).
To conclude, it can be stated that physical activity levels decrease during health crisis restrictions and that these levels are related to well-being. This is due to the release of endorphins inherent to the activity (Martinsen, 2004; Paffenbarger et al., 2004), as well as the triggering of psychological and social mechanisms that are generated when subjects exercise (Andersen et al., 2019; Brière et al., 2018; Espinosa et al., 2015; Siedlecki et al., 2014). No studies have analyzed these variables in Argentina during the pandemic. Additionally, no works have been identified that have methodologically addressed the moderating role of the space where the activity is performed and its modality in the relationship between physical activity and well-being in this context. Therefore, this research aimed to analyze the relationship between physical activity and different dimensions of well-being in the Argentine population during the pandemic, considering the moderating role of the abovementioned variables. It also describes the population’s well-being levels and their levels of physical activity in this health crisis, exploring differences according to the subjects’ sex.
Method
Participants
The sample consisted of 308 subjects, of whom 60.4% were women (n = 186), and the remaining 39.6% were men (n = 122). The mean age was 32.34 (SD = 11.67; minimum = 18; maximum = 64). Of the total sample, 36.4% (n = 99) played sports in open spaces, 25% (n= 68) in enclosed spaces, and 38.6% (n = 105) in both. In addition, 31.2% (n = 86) exercised alone, 33.7% (n = 93) with other person/s, and 35.1% (n = 97) in both ways. A non-probabilistic, purposive, snowball type of sampling was used. The sample selection criteria were that the participants should be between 18 and 64 years of age and that they should be inhabitants of the province of Buenos Aires without any psychiatric diagnosis or severe illness (declared by self-report).
Instruments
Ad Hoc Questionnaire
An ad hoc questionnaire was conducted to collect information on age and sex. It also included questions to explore the space in which you perform physical activity (“When you perform physical activity, do you do it in...”, categorizing responses into four groups: Indoor spaces, Open spaces, Both, I do not perform) and with whom you usually do it (“When you do physical activity, you usually do it...”, categorizing responses into four groups: Alone, With other person/s, Both, I do not perform).
Pemberton Happiness Index (PHI)
The Pemberton Happiness Index Scale (Hervás & Vázquez, 2013) was applied to collect the data corresponding to well-being. The original scale comprises two subscales: remembered well-being and experienced well-being. According to the Argentine adaptation (Delfino et al., 2019), only the first subscale was applied, disregarding the negative affect item. Thus, the remembered well-being scale comprises ten items, integrating general, hedonic, eudaemonic, and social well-being. Cronbach’s Alpha of the scale in the present investigation was α = .88.
International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ)
For the variable corresponding to physical activity, the short version in Spanish (Argentina) of the International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ) retrieved from the IPAQ website (www.ipaq.ki.se) was used. The questionnaire has shown international validity and reliability (Bauman et al., 2011; Craig et al., 2003; Rosenberg et al., 2008). It assesses the frequency (days per week), duration (time per day), and intensity (light, moderate, or vigorous) of activity performed in the last seven days in terms of metabolic rate units (METs) consumed. METs is a unit of energy consumption of the activity that is calculated by multiplying the weekly minutes of physical activity by eight if it is intense, by five if it is moderate, and by 3.3 if it is walking. To calculate the weekly METs consumption, the METs consumed in each of the dimensions of physical activity are added together. Thus, a classification into three groups can be obtained according to how much physical activity is performed weekly: low (0 to 599 METs), moderate (600 to 2999 METs), and high (3000 METs or more). The short version consists of seven questions that provide information on time spent walking, sedentary activities, and moderate and vigorous intensity activities. The participant had to indicate how many days, hours, and minutes per day he/she performed specific physical activity during the last seven days. This version is also valid and reliable (Mantilla Toloza & Gómez-Conesa, 2007).
Procedure
The research responds to a quantitative, non-experimental, descriptive-correlational, cross-sectional design. The questionnaires were administered online, and a web link was distributed to a form created on the Google Forms platform. The link was distributed among university students, who forwarded it to close contacts. Before starting the survey, participants were required to sign an informed consent form, which complied with the guidelines for ethical behavior in the Social and Human Sciences established by the National Council for Scientific and Technical Research (CONICET) of Argentina (Res. D N° 2857/06), in which they were informed about the purposes of the research. All scales were completed individually, and participants did not receive financial compensation.
Data analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using IBM SPSS software, version 25. The sample results were processed to elaborate descriptive statistics and discard possible outliers. Percentages, means, and standard deviations were reported as appropriate. Pearson’s r-test was applied to analyze the association between well-being and physical activity regarding METs consumed weekly. To explore the differences in the levels of physical activity and well-being according to the sex of the subjects, Student’s t-test was used. The one-factor ANOVA test was used to compare the levels of well-being in its different dimensions as a function of the classification into three groups according to weekly METs consumption and to explore the differences in the levels of well-being according to the space in which the physical activity is performed and with whom it is performed. The effect size was calculated for each of the contrasts performed, Cohen’s d statistic was used for the Student’s t-test, and Cohen’s f statistic was used for the ANOVA. The statistical package G*Power v. 3.1.9.2 (Cárdenas Castro & Arancibia Martini, 2014; Faul et al., 2009) was used to perform these calculations. Finally, to examine the possible moderating effect of the space in which you perform physical activity and with whom you usually do it on the relationship between weekly METs consumption and well-being, the PROCESS macro (model 1) for SPSS developed by Hayes (2017) was applied. This macro allows for the performance of a regression-based path analysis. Specifically, the model used analyses the influence of the space in which you are physically active and with whom you usually do it (moderators separately) on the effect size of weekly METs consumed and levels of well-being.
Results
Levels of physical activity and well-being
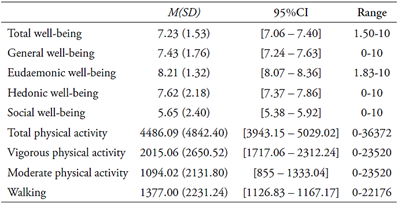
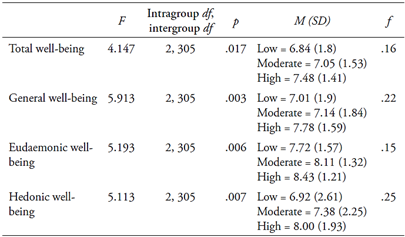
When analyzing the levels of well-being, it was found that the highest mean was concerning personal development and growth, understood as eudaemonic or psychological well-being, and the lowest was the valuation of the circumstances and functioning of society, understood as social well-being. As for the level of physical activity, the subjects were classified according to the weekly METs consumed. The results showed that 13% (n = 40) were placed in the low activity group, 38.3% (n = 118) in the moderate activity group, and 48.7% (n = 150) in the high activity group. Table 1 presents descriptive statistics.
Physical activity and well-being
The levels of the different dimensions of well-being were compared based on the number of METs consumed weekly by physical activity. Differences were found in all dimensions of well-being except Social Well-being [(F (2,305) = 0.91; p = .913)]. The results of the tests can be seen in Table 2 (in all cases, the post-hoc test used was Dunnett’s T3). In all cases, subjects classified as highly physically active presented higher levels of well-being.
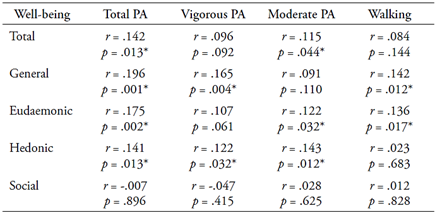
Total METs consumed weekly correlated positively with total, general, eudaemonic, and hedonic well-being dimensions (see Table 3). The vigorous physical activity presented a positive correlation with general and hedonic well-being. The moderate physical activity dimension positively correlated with total, eudaemonic, and hedonic well-being. In turn, the METs consumed weekly in walking were positively correlated with general and eudaemonic well-being. In all cases, the correlation coefficients show a low-intensity association. The levels of social well-being did not show a significant association with any of the dimensions of physical activity.
Table 2 Values of the one-factor ANOVA test for significant differences in well-being according to the classification of METs consumed weekly
Differences in levels of physical activity and well-being by sex
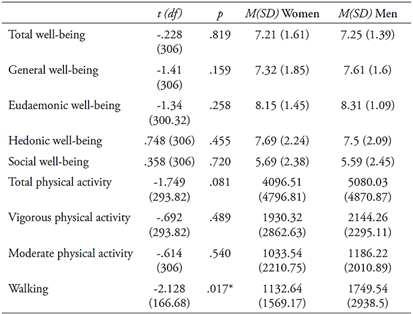
When exploring differences in the levels of well-being and physical activity according to the subjects’ sex, significant differences with a small-medium effect size (d = .27) were only found in the dimension of METs consumed weekly in walking, with men walking more than women. The remaining dimensions of physical activity and none of the dimensions of well-being presented significant differences according to the subjects’ sex (see Table 4).
The moderating role of the physical space in which physical activity is performed
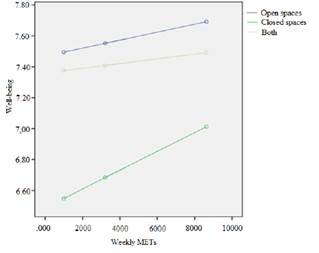
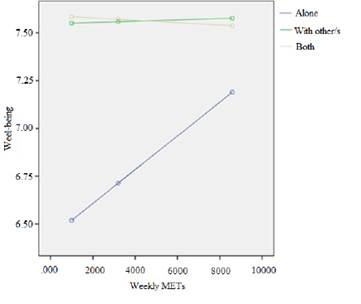
Differences were verified with a medium effect size in the levels of total well-being as a function of the space in which they perform physical activity [F (2, 269) = 8.527; p < .001; M (SD): Closed spaces = 6.7 (1.81), Open spaces = 7.59 (1.22), Both = 7.44 (1.31); f = .24; Post-hoc test: Dunnet’s T3]. Those who did it in open spaces present higher levels of well-being. In order to understand the moderating role of space in the relationship between weekly METs and levels of well-being, a moderation analysis was performed. Table 5 shows the results of the moderation analysis. When comparing the strength of the relationship between weekly METs consumed and the level of total well-being as a function of the space in which the physical activity is performed, it is observed that subjects who perform it in open spaces (either exclusively in open spaces or in open and closed spaces) present higher levels of well-being than those who perform it only in closed spaces. It should be noted that, in all cases, increasing the frequency of weekly physical activity increases the perceived levels of well-being. Figure 1 summarizes the results of moderation.
Table 5 Results of the analysis of the moderating role of physical activity space in the relationship between METs consumed weekly and total well-being
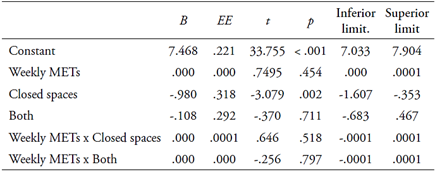
Note: B: non-standardized regression coefficient; EE: standard error. R2 = .0704, F (5. 266) = 4.0312, p = .0015.
The moderating role of physical activity modality (individual, with other/s, and both)
Differences were verified with a medium effect size in the levels of well-being according to whether they performed physical activity alone or accompanied [F (2.273) = 8.619; p = < .001; M (SD): Alone = 6.78 (1.71), With other person/s = 7.56 (1.27), Both = 7.55 (1.28); f = .24; Post-hoc test: Dunnet’s T3]. Those who exercised with another person/s presented higher levels of well-being. In order to explore the moderating role of the company or not of other people in the relationship between weekly METs and levels of well-being, a moderation analysis was performed. Table 6 shows the results of the moderation analysis. When comparing the strength of the relationship between the METs consumed weekly and the level of total well-being depending on whether the physical activity is performed alone or accompanied, it is observed that the subjects who perform it accompanied (either exclusively accompanied or sometimes alone and sometimes accompanied) present higher levels of well-being than those who do it alone. It should be noted that, especially in the case of subjects who do physical activity alone, the frequency of weekly physical activity produces a more significant increase in levels of well-being. Figure 2 summarizes the results of moderation.
Table 6 Results of the analysis of the moderating role of the company in physical activity on the relationship between METs consumed weekly and total well-being
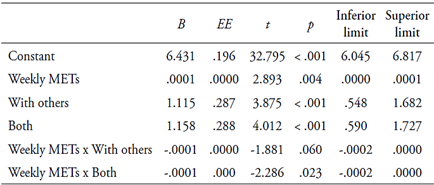
Note. B: non-standardized regression coefficient; EE: standard error. R2 = .0879, F (5, 270) = 5.2031, p = < .001
Discussion
This study aimed to analyze the relationship between physical activity and levels of well-being in the context of a pandemic in Argentine adults over 18 years of age. The results describe the well-being and physical activity levels in this context while analyzing differences according to the subjects’ sex and exploring the moderating role of space and with whom physical activity is generally performed.
The lowest levels of well-being were found in the social dimension for all subjects, coinciding with previous studies in Argentina (Zubieta & Delfino, 2010). No significant differences were found in the levels of well-being by the gender of the subjects. These results differ from previous research in the same context, which reported that women presented higher psychological and social well-being levels than men (Valle Raleig et al., 2019; Zubieta & Delfino, 2010). These results are also inconsistent with a more recent study in which the same well-being measurement instrument was applied, as it was found that men reported higher levels of social well-being and total well-being (Delfino et al., 2019). Men scored higher than women in the levels of METs consumed weekly by walking, which is the only difference found in the amount of physical activity performed. Previous studies in the same context report that men do more physical activity than women in all age groups (González Insua et al., 2020). Therefore, these discrepancies in the results may be because previous studies only considered physical exercise performance and not the different dimensions of physical activity analyzed in this work: intense physical activity, moderate physical activity, and walking. In the study, these dimensions were defined based on the intensity of the activity according to the METs expended. METs are a unit of energy expenditure of the activity calculated by multiplying the weekly minutes of physical activity by 8 if it is intense, by 5 if it is moderate, and by 3.3 in the case of walking.
A positive correlation was found between total energy consumption and levels of well-being, with those subjects who were more active presenting higher levels of well-being. This confirms the findings of previous studies in the same and other contexts (Faulkner et al., 2020; González Insua et al., 2020; Jacob et al., 2020). This relationship may be due to the neurobiological effects of the release of endorphins, which act directly on the brain to produce a feeling of well-being and reduce stress, anxiety, and depression (Martinsen, 2004; Paffenbarger et al., 2004). Additionally, physical activity or exercise can trigger psychological and social mechanisms, such as the development of initiative, teamwork, and self-control, while also facilitating the cultivation of positive and prosocial relationships. These aspects are associated with less discomfort, anxiety, and sadness (Brière et al., 2018).
While physical activity levels were not significantly related to social well-being, this is understandable given that social well-being encompasses aspects such as the possibility of personal growth, trust in the future of society, and living in a society that produces well-being (Keyes, 1998). These aspects are not directly related to the feelings of well-being that are characteristic of the release of endorphins, as mentioned by previous studies (Espinosa et al., 2015; Valle Raleig et al., 2019; Zubieta & Delfino, 2010).
The physical space in which participants perform physical activity was found to be a moderating variable in the relationship between the frequency of physical activity and levels of well-being. Specifically, open spaces were associated with greater well-being than closed spaces. This finding is consistent with previous research (Rogerson et al., 2020; Silva Piñeiro & Mayán Santos, 2016; Thompson Coon et al., 2011). One explanation for this finding is the stress reduction theory (Ulrich et al., 1991), which states that exposure to natural spaces can decrease physiological arousal and negative affect and increase positive affect. Additionally, Marselle et al. (2016) found that walking in natural spaces was associated with higher levels of well-being due to the psychological and physical distance from the burden of cognitive content, effortless attention to environmental stimuli, and unity with the environment. This is consistent with Kaplan’s (1995) theory that natural spaces contain intrinsically fascinating elements that require only moderate attentional capacities, allowing for the recovery of cognitive resources and improved attentional task performance and mood. While the results of this study confirm previous findings, the research mentioned above did not specifically explore the moderating role of the physical space in which physical activity is performed, as has been done in this study.
The person with whom the physical activity is performed was also found to be a moderating variable in the relationship between the frequency of physical activity and levels of well-being. Specifically, performing physical activity exclusively accompanied or in a mixed modality was associated with higher levels of well-being. Subjects who did physical activity alone had a stronger relationship between weekly energy consumption and levels of well-being than those who did it with others or in a combination of both modalities. These subjects had similar levels of well-being regardless of their energy intake. Similarly, subjects with a high energy intake but only did physical activity individually had lower levels of well-being than those who did activity with others with a shallow frequency. This finding is consistent with the results of previous studies (Almeida et al., 2018; Lovell et al., 2016; Werneck et al., 2021). Physical activity in groups is associated with increased life satisfaction, coping capacity, and decreased negative affect (Siedlecki et al., 2014). This is likely because group physical activity provides a social environment where participants can interact meaningfully and inclusively (Andersen et al., 2019). Therefore, social mechanisms such as perceived social support can explain the association between well-being and group physical activity.
It is important to note that the data was collected during the COVID-19 pandemic. This may have influenced the moderating role of the two variables, as people may have been more motivated to be in open spaces and with other people during the confinements and quarantines that were put in place to prevent the spread of the virus. Therefore, it is possible that the intensity and frequency of physical activity were not the main factors associated with well-being in this context, but rather the opportunity to be outside and to socialize with others. In summary, the findings of this study underscore the significant influence of physical environment and socialization degree on the relationship between physical activity and well-being. These findings emphasize the importance of promoting physical activity in natural environments and encouraging participation in groups, not only to enhance individual well-being but also to provide essential social and emotional support, especially in times of crisis such as the COVID-19 pandemic. These results support the need to consider these factors in the design of public health policies and programs aimed at improving the well-being of the general population, emphasizing the importance of providing access to open spaces and opportunities for physical activity in inclusive social environments.
Although physical activity is widely considered a therapeutic tool for treating depression and anxiety, there is still much we do not know about the ideal characteristics of this activity. For example, do the benefits of physical activity vary depending on whether it is done in groups or open spaces? What is the ideal dose of physical activity regarding frequency and intensity? Moreover, do the results of physical activity interventions differ in clinical populations or those with chronic diseases? Finally, what is the impact of physical activity on the well-being of adults over 65?
The study has several limitations. First, self-reporting physical activity may have introduced reporting biases, such as social desirability or retrospective bias. Second, the descriptive-correlational design of the study does not allow us to determine whether physical activity has a causal effect on well-being. Future studies should use objective measures of physical activity and experimental designs to address these limitations.