BACKGROUND
Since 2019 the world has been facing the COVID-19 pandemic, a disease caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus and its variants (Gobierno de Mexico, 2020). This global phenomenon has caused changes in lifestyle and types of social interaction, in addition to producing an increase in mental disorders such as depression, anxiety, substance abuse, suicide, and stress (Dong & Bouey, 2020; Organización Panamericana de la Salud (PAHO), 2020; Talevi et al., 2020).
The most representative psychosocial effects of this pandemic include loss of daily activities, reduced social contact, unemployment, violence, financial problems, a saturation of hospitals, poor access to health services, and alterations in mental health, particularly in vulnerable groups such as children, adolescents, and women (Organización Mundial de la Salud (OMS), 2021; Entidad de las Naciones Unidas para la Igualdad de Género y el Empoderamiento de las Mujeres (ONU Mujeres), 2020 a; Parisi et al., 2021; Rajkumar, 2020; Torales et al., 2020).
According to Barzilay et al. (2020), stress is a frequent problem in women during this pandemic due to the overload of domestic, work, or school activities, caring for a family member with COVID-19, financial debts, or unemployment. These problems increase stress levels and are related to non-adaptive coping styles and resilient behaviors (Backhaus et al., 2021; Yildirim & Arslan, 2020). Also, Lai et al. (2020) suggest that the stress derived from facing the pandemic is usually intense in those people who are informed of its progress, adhere to health regulations, and have had a sudden loss of rewarding activities.
These situations can produce unhealthy behaviors in women, for example, consumption of alcohol and other drugs, smoking, sedentary lifestyle, reduction in physical activity, and physical violence (Almeida et al., 2020; Capasso et al., 2021; Czeisler et al., 2020; Fondo de Población de las Naciones Unidas (UNFPA), 2020 a; Pieh et al., 2020; Sediri et al., 2020; ONU Mujeres, 2020 b).
A study carried out by Pérez et al. (2021) revealed that the most frequent emotional responses in a sample of 174 Mexican women (M = 37.72 years) were anxiety and stress, 72.4% of the women requested psychological support to attend to psychosocial needs at the beginning of the Nueva Normalidad stage due to interpersonal problems and task overload.
Tharp et al. (2021) found that socioeconomic status and marital status are not variables that are related to stress, however, the gender role is due to the activities expected in men and women. Other studies reveal that perception of less stress is related to greater resilience and the implementation of adaptive coping styles, in addition to other variables such as educational level and the professional situation in the case of women (Abbott et al., 2021; Lindinger-Sternart et al., 2021). The evaluation of stress responses in women is a problem of public health interest because during this health emergency they have experienced a greater number of psychological problems and/or severity of symptoms associated with mood disorders, compared to men. This situation has led to the idea that women are a vulnerable group for the development of mental disorders, in addition to the active role they have played in times of COVID-19 (Almeida et al., 2020; González-Ramírez et al., 2020; National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH), 2020; Rodríguez-Bermúdez et al.,2021). The aim of this study was to evaluate the relationship between stress levels, knowledge about COVID-19, ways of coping, and resilience in a sample of Mexican women.
METHOD
Design
A non-experimental, cross-sectional, and correlational study was carried out (Kerlinger & Lee, 2001).
Participants
Through a non-probabilistic snowball sampling, 386 women from Mexico City and the metropolitan area participated voluntarily. The mean age was 40.69 years (SD = 13.18; Mo = 23.0). The inclusion criteria to participate in the study were: being a Mexican woman, having an email account, having a device with internet access (smartphone, tablet, computer, or laptop), and residing in one of the states of the country. Exclusion criteria: be a minor (be under 18 years of age), report a psychological and/or psychiatric diagnosis in the online evaluation, or be under treatment of this nature.
Instruments
Socio-demographic data card. Set of five items that collect information on age, marital status, educational level, occupation, and location.
COVID-19 Knowledge Questionnaire. Prepared for research purposes (ad hoc). Consisting of seven statements on the forms of transmission, prevention, and identification of symptoms, with a true and false response format. The correct options were coded with one and the incorrect ones with zero. For the present study, the discriminative power and difficulty index of the test were obtained according to Robles and Díaz-Loving (2011) proposal. The results revealed that item seven (χ2 (1) = 2.766; p = .266) did not discriminate between participants who obtained a low and high score, so the decision was made to reduce the scale to six items, with this modification the difficulty index was .294.
Perceived stress scale (PSS-14). Consisting of 14 items with five response options on a Likert-type scale (never, rarely, occasionally, often, and very often) that assesses the level of perceived stress. Adapted and tested in the Mexican population by González and Landero (2007) showing an acceptable internal consistency (α = .83), which explains 48.02% of the variance. A confirmatory factor analysis was performed with the data from this sample and the scale showed a good fit (χ2 (13) = 39.493, p = .000; χ2 / gl = 3.0, RMSEA = .073, (CI = .047-, 099); CFI = .971; TLI> .952) by eliminating items 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, 10 and 13, leaving only seven items that explain 43.2% of the variance, with α = .837 and Ω = .837.
Ways of Coping Questionnaire (WCQ). Consisting of 20 questions, with four response options on a Likert-type scale (never, not at all, to some extent, generally, usually, and always) that assesses the styles of coping with the stress produced by daily life situations, to through five factors: evasive confrontation, positive appraisal, distancing, denial, and reflexive-cognitive analysis. The instrument was adapted and validated in the Mexican population by Zavala et al. (2008), with an α = .85. In the confirmatory factor analysis carried out with the present sample, items 1, 7, 13 and 17 had to be eliminated to achieve an acceptable fit of the scale (χ2 (192) = 199.564, p = .000; χ2 / gl = 2.2, RMSEA = .055, (IC = .045-.066); CFI = .926; TLI = .904), with 16 items that explain 34.8% of the variance, with α = .771 and Ω =. 905.
Mexican Resilience Scale. This scale was created by Palomar and Gómez (2010) to measure resilience in the Mexican population, it is composed of 43 items grouped into five factors (strength and self-confidence, social competence, family support, social support, and personal structure) that according to their authors explain 43.609% and an acceptable internal consistency coefficient (α = .93). Which answered on a four-point Likert-type scale (totally disagree, disagree, agree, and totally agree). In the analysis with the present sample, an acceptable fit of the scale was observed (χ2 (845) = 1778.186, p = .000; χ2 / gl = 2.1, RMSEA = .054, (IC = .050-.057); CFI = .915; TLI = .909), which explains 53.9% of the variance, with α = .963 and Ω = .980.
Procedure
The evaluation was implemented on the Google-Forms Online® platform (composed of the informed consent form, the sociodemographic data card, the COVID-19 knowledge questionnaire, and the psychometric scales) and was disseminated via social networks such as Facebook® and WhatsApp® between June 25 and October 23, 2020, when Mexico found itself in Phase 3 of the pandemic, half of the national territory was at a red epidemiological traffic light, the Jornada Nacional de Sana Distancia had concluded (closure of schools, work centers, and confinement) and had begun with the return to the Nueva Normalidad, thus determined by the Secretaria de Salud (SSa, 2020). Mexico was still in the first wave of COVID-19, where figures of between close to 3,000 and more than 28,000 new accumulated cases were obtained and between 100 and 900 deaths were registered (SSa, 2020).
Statistical analysis
The data were analyzed with the statistical program SPSS® version 24 and AMOS 25 for Windows®. It began with the descriptive analysis of the variables to have a summary of the characteristics of the participants, in addition to obtaining the asymmetry indices (<1.5), kurtosis (<1.5), and the critical ratio of multivariate kurtosis (<7.00; Hong et al., 2020), to determine the normality in the distribution of the data and with it the type of statistic to use.
A Confirmatory Factor Analysis (CFA) was performed for each instrument used, given that the factorial structure was already known, the adjustment indices were considered as criteria using the standardized regression weighting (factor loadings) and the adjustment indices: chi-square (χ2, p> .05), quotient resulting from χ2 / gl, (<3), mean square error of approximation (RMSEA <.08, 90% CI), comparative fit index (CFI> .90) and Index of Tucker-Lewis (TLI> .90; Pérez et al., 2013). The internal reliability of the measurements was examined using Cronbach's alpha (α) and the omega coefficient (Ω).
Subsequently, the relationship between variables was analyzed with Pearson's r statistic, incorporating the Bootstrapping and 95% Bias-corrected, accelerated (BCa) with 1000 samples. This procedure was considered due to the total sample, also, it was segmented into groups with high and low levels of stress (high and low quartile), the latter to know its degree of involvement in the general correlation. Finally, to know the relevance of the differences found, Cohen's q statistic was calculated, under the procedure proposed by Ventura-León and Caycho (2017).
Ethical considerations
The participants completed the form after giving their informed consent, in which reasonable and understandable language was used. If the participants agreed, they clicked on the “Yes, I accept” option, displaying a new window with the questionnaire questions. On the other hand, if they chose the “I do not accept” option, a Window was displayed thanking them for their time and the form ended.
The form indicated that the processing of personal data would be confidential, anonymous, and for scientific research purposes. Unjustified or delayed data collection procedures were always avoided, and personal data was safeguarded. This research was approved by UN Women and was part of a specialized consultancy subject to methodological and ethical review with the number SSA / CI 006-20. Given the increase in scientific research that collects data with the use of social networks in the context of the pandemic, the standards of the Code of Ethics for Psychologists (Sociedad Mexicana de Psicología, 2014) and the suggestions of the Guide for the Practice of Psychology were used. Telepsychology (American Psychological Association, 2013).
RESULTS
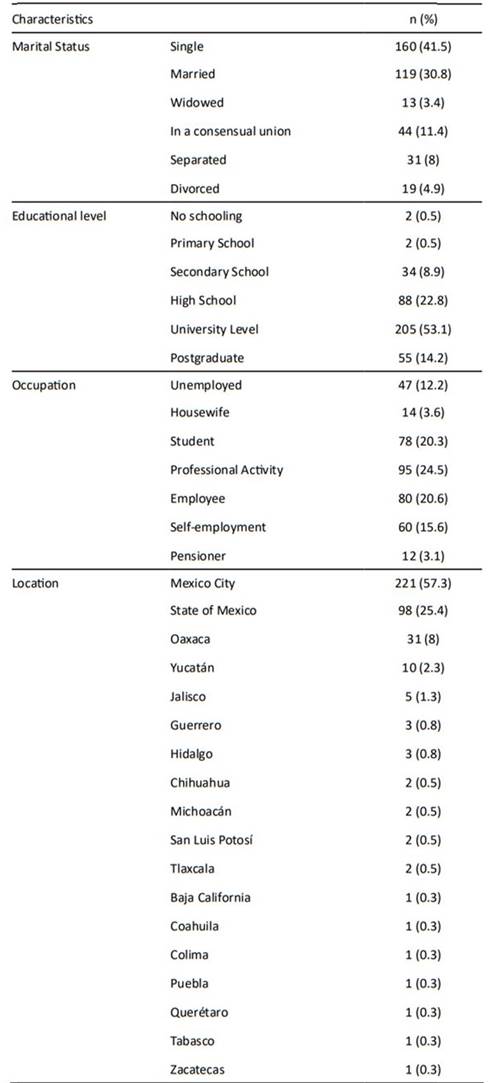
The sociodemographic characteristics of the participants are shown in Table 1. Most of the participants were single (41.5%), married (30.8%), and 53.1% had superior studies and at the time of this research they were engaged in professional activity (24.4%), were employees of an institution (20.5%) or students (20.2%).
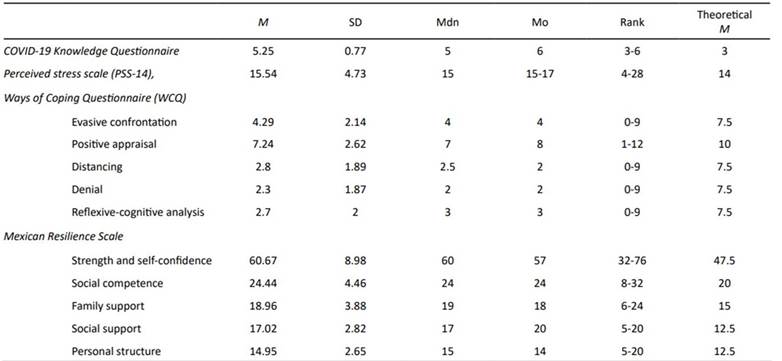
The participants demonstrated having information related to COVID-19, associated risk factors, and preventive measures, they answered correctly almost all the questions evaluated in the COVID-19 Knowledge Questionnaire. They reported having moderate levels of stress (M = 15.54; Theoretical M = 14) and in terms of coping, they scored below the mean in all factors including positive appraisal as observe in Table 2. Finally, in the resilience variable, scores above the mean were obtained in all subscales, strength and self-confidence being the subdimension with the most distant data (M = 60.67, SD = 8.98, Theoretical M = 47.5). These results show a high resilient self-perception for each area.
Table 2 Analysis of the scores obtained on the scales: COVID-19 Knowledge Questionnaire, Perceived stress scale (PSS-14), Ways of Coping Questionnaire (WCQ), and Mexican Resilience Scale.
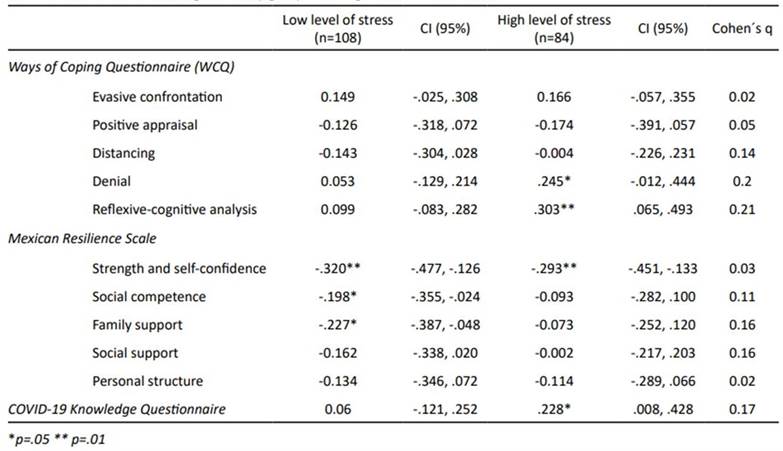
The results obtained in the segmented correlation analysis indicate that the forms of coping are related in a different way between women who live with a low level of stress versus those who live with a high level. Elevated stress levels are positively and significantly related to the factor denial (r = .245; p = <. 05) and reflexive-cognitive analysis (r = .303; p = <. 01) as shown in Table 3. The higher the level of knowledge about COVID-19, the greater the stress (r = .228; p <.05). Despite the statistically significant association, the effect size for the three variables was small as reported by Cohen's q = .20, .21, and .17 respectively.
On the other hand, low levels of stress are negatively associated with the factors of the resilience scale, strength and self-confidence (r = .320; p = <. 01; q = .03), social competence (r = .198; p = <. 05; q = .11) and family support (r = .227; p = <. 05; q = .16). It should be noted that the only variable that behaved similarly in both groups was strength and self-confidence.
DISCUSSION
The findings of this study suggest that the participants have information about COVID-19, hygiene rules, and social interaction, while also reporting experiencing moderate levels of stress. In this regard, studies such as those by Lai et al. (2020), Rajkumar (2020), and Torales et al. (2020) suggest that the stress derived from living under a pandemic can be exacerbated in those who are informed, follow health regulations, and decrease the frequency of performing pleasant activities.
In addition, it must be considered that during the evaluation period between June and October 2020, the cases of morbidity and mortality from COVID-19 were increasing, so the general population should try not to leave home, restricting themselves only to first-class activities. need and go out only if there is a need to do so (SSa, 2020).
This situation could have had repercussions on the state of mind and the level of stress in the general population (González-Ramírez et al., 2020; Rodríguez-Bermúdez et al., 2021). Consistent with this situation, the results suggest that being informed about this health emergency, following the recommendations established by the health authorities, and the prolongation of the pandemic triggered stress responses in the women in this sample.
In addition to these conditions, most of the participants were studying or working from home or were unemployed, while doing domestic and/or care work. According to Almeida et al. (2020), Czeisler et al. (2020), Pérez et al. (2021), Pieh et al. (2020), and Sediri et al. (2020), these and other functions that have been associated with the gender role have caused women to experience high levels of anxiety and stress. Although this research did not investigate whether compliance with activities attributed to the gender role was related to stress, studies and reports carried out during the first phases of the pandemic have indicated that the mental health of women has deteriorated significantly, due to the increase in work and domestic tasks they perform (Pérez et al. (2021; Rodríguez-Bermúdez et al., 2021 Rodríguez-Hernandez et al., 2021; Tharp et al., 2021).
Concerning the coping evaluation, it was found that in all the subscales the participants scored below the average, even in the positive factor positive reappraisal, this result suggests that they have an active coping not only with specific stressors but also in those that arise in the normal course of the pandemic (Capasso et al., 2021; Parisi et al., 2021; Pérez et al., 2021).
Regarding the resilience variable, in all the subscales of this construct, there are scores above the average, therefore, the women in this sample perceive that they can interact and cope adequately in their context even in crises preserving family ties, which translates into moving towards their life purpose even after a traumatic event (Backhaus et al., 2021). Although low levels of stress were negatively but statistically significantly associated with factors such as social competence, family support, and strength and self-confidence, the effect size was small, which could indicate that the assessment of life-threatening events in daily life and those associated with the pandemic result in the search for social support and resilient behaviors. It would be worth discussing the implications of the use of coping strategies such as denial and cognitive-reflexive analysis in women with high stress because even when they perceive themselves as resilient, it does not necessarily translate into a better way of coping with problems, consequently causing, long-term havoc on their mental health (Capasso et al., 2021; Lai et al., 2020).
Even though the adverse effects of the pandemic on mental health and resilience have been hypothesized, the impact it has is still unknown as it is a changing and long-lasting event. Therefore, it is vital to make exhaustive assessments considering the different moments of this pandemic and its effects on women (National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH), 2020; ; UNFPA, 2020 b). Although variables such as educational level and professional situation were related to high resilience (Abbott et al., (2021; Lindinger-Sternart et al., 2021), it is worth continuing to develop research on women with other characteristics.
Finally, it is highlighted that this research indicates the need to evaluate the possible effects on the mental health of vulnerable social groups in a health emergency. This is to provide timely psychological and/or psychiatric care adjusted to the needs of the population (Dong & Bouey, 2020; Torales et al., 2020; Organización Panamericana de la Salud (PAHO), 2020).
Some of the limitations of this study did not include aspects related to gender role, associated activities, and whether this is a variable that predicts stress, coping strategies, or resilience. Another limitation is associated with the course of the pandemic itself and the evaluation period, since this study was cross-sectional, it was not possible to evaluate the changes in the variables studied over time. In this regard, given the evolution of the pandemic, the needs and problems experienced may be different, so the situations perceived as stressful may also have changed (Rubin et al., 2010). Finally, the application of psychological instruments in online mode is usually considered inaccurate or methods where the self-report of some variables is overestimated. However, there is also evidence of its usefulness, functionality, and equivalence between these forms and those used traditionally (Pérez-Bautista & Lugo-González, 2022; Weigold et al., 2013).
It is concluded that women perceived themselves as having high resilience, however, they present moderate stress levels, having more information about COVID-19 was associated with greater stress. High-stress levels are related to denial and reflective cognitive coping styles. Resilience was associated with low levels of stress, so increasing it would help reduce the levels of those who were most affected.
It is suggested for future research to include both sexes, to carry out a longitudinal study that allows knowing the changes in the levels of stress, resilience, and the coping styles that are used to face the situations that arise during the COVID-19 pandemic, given that this health emergency is not over yet. To investigate if the gender role plays a role in the mental health of women and men is the proposal.