Servicios Personalizados
Revista
Articulo
Indicadores
-
 Citado por SciELO
Citado por SciELO
Links relacionados
-
 Similares en
SciELO
Similares en
SciELO
Compartir
Revista Peruana de Medicina Experimental y Salud Publica
versión impresa ISSN 1726-4634versión On-line ISSN 1726-4642
Rev. perú. med. exp. salud publica vol.40 no.4 Lima oct./dic. 2023 Epub 18-Dic-2023
http://dx.doi.org/10.17843/rpmesp.2023.404.13261
Letter to the editor
Cyclone “Yaku” and Leptospira serovars in La Libertad, Peru
1 Human Medicine Study Program, Private University Antenor Orrego, Trujillo, Peru.
2 La Libertad Regional Referral Laboratory, Trujillo, Peru.
3 Department of Science, Private University Antenor Orrego, Trujillo, Peru.
To the Editor. Climate change has impacted Peru in the form of phenomena such as “El Niño”, or the “Yaku” cyclone, which have affected the northern Peruvian coast during 2023. These events have increased temperatures and precipitation, which are related to negative impacts on health 1. The high incidence of rainfall caused by these phenomena increases the probability of contact with rodents, the natural reservoirs of Leptospira spp., causing contamination of water bodies and soils with these bacteria 2. For this reason, this study aimed to characterize Leptospira serovars in the La Libertad region, between January and March 2023, in the context of cyclone “Yaku”.
Leptospirosis is one of the most prevalent zoonotic diseases, with high prevalence in tropical areas and a high morbidity rate and thousands of deaths reported annually 2. In this scenario, 5123 cases of leptospirosis were reported in Peru during 2022, with 29 cases detected in La Libertad 3. The Microscopic Agglutination Test (MAT) was used to detect the cases, which is considered to be the gold standard for the diagnosis of leptospirosis due to the taxonomic complexity of the genus Leptospira spp. 4.
Between January and March 2023, during cyclone “Yaku”, 163 samples from patients with presumptive diagnosis of leptospirosis were analyzed at the Regional Referral Laboratory of La Libertad (LRRLL). We report the serological evidence of infection; for this we selected the files with results of the IgM Enzyme-Linked Immunoadsorption Assay (IgM ELISA) reactive for Leptospira. The tests were performed at the LRRLL. Samples with reactive results were screened for MAT evaluation at the National Referral Laboratory for Bacterial Zoonoses of the National Institute of Health in order to determine the serovars with the highest prevalence. The data are presented in Figure 1.
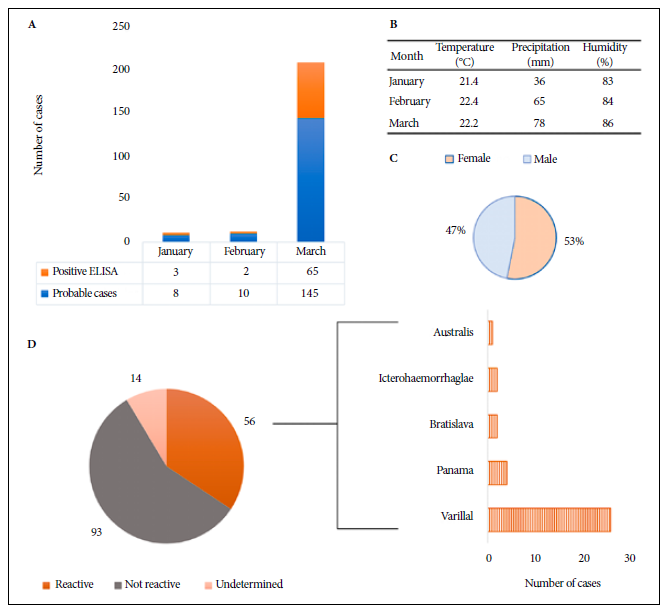
Figure 1 Analysis of Leptospira spp. cases at the Regional Referral Laboratory of La Libertad. (A) Probable and positive cases according to ELISA test. (B) Meteorological data on temperature (°C), precipitation (mm) and humidity (%) in La Libertad region. (C) Composition of patients according to sex. (D) MAT results for serovars Varillal, Panama, Bratislava, Icterohaemorrhagiae and Australis.
The results show 70 reactive cases screened by ELISA (Figure 1A). Of these, 65 cases were reported in March, coinciding with the highest precipitation rates, according to meteorological data (Figure 1B). Forty-seven percent of the samples were obtained from male patients, while 53% were obtained from females (Figure 1C). The ELISA test yielded positive results for 56 cases and the most prevalent serovars when processed by MAT were Varillal (37%), Panama (5.7%), Bratislava (2.9%), Icterohaemorrhagiae (2.9%) and Australis (1.4%), as shown in Figure 1D.
The increase of leptospirosis cases during the month of March was probably related to the climatic conditions surrounding cyclone “Yaku”, with high temperatures and increases in environmental humidity, conditions in which, according to Yanagihara et al. 5, bacteria of the genus Leptospira spp. are able to persist indefinitely. Moreover, similar results were reported by Serrano-Martínez et al. 6, who found a high prevalence rate of Leptospira spp. infection under conditions of high humidity and temperature during the spring and summer seasons. In fact, the prevalence of leptospirosis was found to be 28.9% in a district of Chiclayo between October and December 2016 7. Most samples analyzed at LRRLL were associated with the Varillal serovar, which coincides with a study conducted at the Public Health Reference Laboratory of Jaén that reported a higher incidence of the Varillal and Icterohaemorrhagiae serovars under climatic conditions of high rainfall and humidity 8. In this context, climatic phenomena such as the cyclone “Yaku” could have serious consequences on public health by providing ideal conditions for the dissemination of infectious agents such as Leptospira spp.
The limitations of this study include the fact that MAT was only performed on samples with reactive ELISA results and the presence of only one sample from each patient in the MAT, which limits the study to probable cases according to Health Directive N° 065-MINSA/DGE-V.01. The specific diagnosis of this disease is performed by MAT, polymerase chain reaction (PCR), or bacteriological culture, but these methods are limited by their complexity in order to be implemented. Furthermore, this study does not reflect the magnitude of leptospirosis in the La Libertad region because this was not a prevalence study. Finally, although we found an increase in the number of cases during the study period, specific studies are needed to associate and correlate the magnitude of the influence of climate change with the appearance of leptospirosis.
In conclusion, the number of leptospirosis cases increased when cyclone “Yaku” appeared, mostly during March, which is when the cyclone impacted La Libertad region. In this context, it is important to note that most Leptospira infection cases were due to the Varillal and Panama serovars, therefore we consider that it is necessary to adopt promotion and prevention measures, avoiding their spread and contributing to improve public health in Peru. These measures should include the development of rapid immunochromatographic tests of high sensitivity and specificity that can be applied at the first level of care, especially under adverse weather conditions.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the Universidad Privada Antenor Orrego for providing the necessary time and the Laboratorio Referencial Regional de La Libertad for providing the data for this publication.
REFERENCES
1. Blanco-Villafuerte L, Hartinger SM. Impacto del cambio climático en la salud de los peruanos: desafíos y estrategias para una respuesta integral. Rev Peru Med Exp Salud Publica. 2023;40(2):130-1. doi: 10.17843/ rpmesp.2023.402.12998. [ Links ]
2. Rahelinirina S, Bourhy P, Andriamiaramanana F, Garin B, Rajerison M. High Prevalence of Leptospira spp. in Rodents in an Urban Setting in Madagascar. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2019;100(5):1079-81. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.18-0642. [ Links ]
3. Centro Nacional de Epidemiologia, Prevención y Control de Enfermedades. Número de casos de leptospirosis, Perú 2018 - 2023 [Internet]. Lima; 2023 [citado el 25 de julio de 2023]. Disponible en: https://www.dge.gob.pe/portal/docs/vigilancia/sala/2023/SE03/leptospirosis.pdf. [ Links ]
4. Pinto GV, Senthilkumar K, Rai P, Kabekkodu SP, Karunasagar I, Kumar BK. Current methods for the diagnosis of leptospirosis: Issues and challenges. J Microbiol Methods. 2022;195:106438. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2022. [ Links ]
5. Yanagihara Y, Villanueva SYAM, Nomura N, Ohno M, Sekiya T, Handabile C, et al. Leptospira Is an Environmental Bacterium That Grows in Waterlogged Soil. Microbiol Spectr. 2022;10(2):e0215721. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02157-21. [ Links ]
6. Serrano-Martínez E, Burga Cisterna C, Hinostroza M. E, Zúñiga FR. Influencia de las estaciones climáticas en la presencia de leptospirosis canina en el norte y centro de Lima, Perú. Revista de Investigaciones Veterinarias del Perú. 2020;31(4):e19018. doi: 10.15381/rivep.v31i4.19018. [ Links ]
7. Yamunaqué-Castro LA, Aguilar-Gamboa FR, Quenema-Díaz EA, Becerra-Gutiérrez LK, Silva-Díaz H. Seroprevalencia de brucelosis y leptospirosis en pobladores urbanos con crianza traspatio en el distrito de José Leonardo Ortiz de Chiclayo. Revista Medica Herediana. 2020;31(1):30-6. doi: 10.20453/rmh.v31i1.3725. [ Links ]
8. Alvarado Dávila X, Gavidia Olivera EY, Zulueta Vásquez BN, Romaní F. Leptospirosis en pacientes con resultado negativo para dengue, zika y chikungunya en Jaén, Perú. Rev Peru Med Exp Salud Publica. 2019;36(3):535. doi: 10.17843/rpmesp.2019.363.4457. [ Links ]
Received: September 06, 2023; Accepted: December 15, 2023











 texto en
texto en 



