INTRODUCTION
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) infection is a current public health problem. In 2021, 38,4 million people were infected worldwide, with an incidence of 1.5 million 1. The rapid spread of the disease represents a major challenge for developing countries, as they face economic and logistical shortcomings to diagnose cases in a timely manner. 1
In Latin America and the Caribbean, it was estimated that 120,000 people were infected with HIV in 2021, representing a significant increase of 7,5% compared to 2010. The largest increases occurred in Brazil (21%), Costa Rica (21%), Bolivia (22%) and Chile (34%). At the same time, significant decreases were observed in El Salvador (-48%), Nicaragua (-29%), Colombia (-22%) and Peru (-6%). 2
The confirmatory test for the diagnosis of HIV, according to the World Health Organization (WHO), are the Immunoblot, Line Immunoassay (LIA) and Indirect Immunofluorescence (IFI) tests, within the screening tests are used 4th generation enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), the application of these diagnostic tests requires an optimal infrastructure, as well as appropriate equipment and reagents. 3
During the pandemic period, not only did COVID-19 disease generate a break in public health, but also various diseases such as HIV/AIDS that were not diagnosed, treated, or controlled. For this reason, the study aimed to evaluate the control of viral load and lymphocyte load in the resident population of Callao with a confirmed diagnosis of HIV, during the Covid 19 pandemic. 4
METHODS
Study design and sample selection
Retrospective cohort study in which the data were selected from samples processed at the Laboratorio de Referencia Regional de Infecciones de Transmisión Sexual y Metaxénicas (LRRITSYM) of DIRESA-Callao previously analysed for HIV by Indirect Immunofluorescence (IFI) and 4th generation enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) in the period from 2021 to 2022. The LRRITSYM as a public laboratory receives daily blood samples that come through requests from all hospitals and health centres in the Callao region for the diagnosis, control and monitoring of HIV.
Statistical Analysis
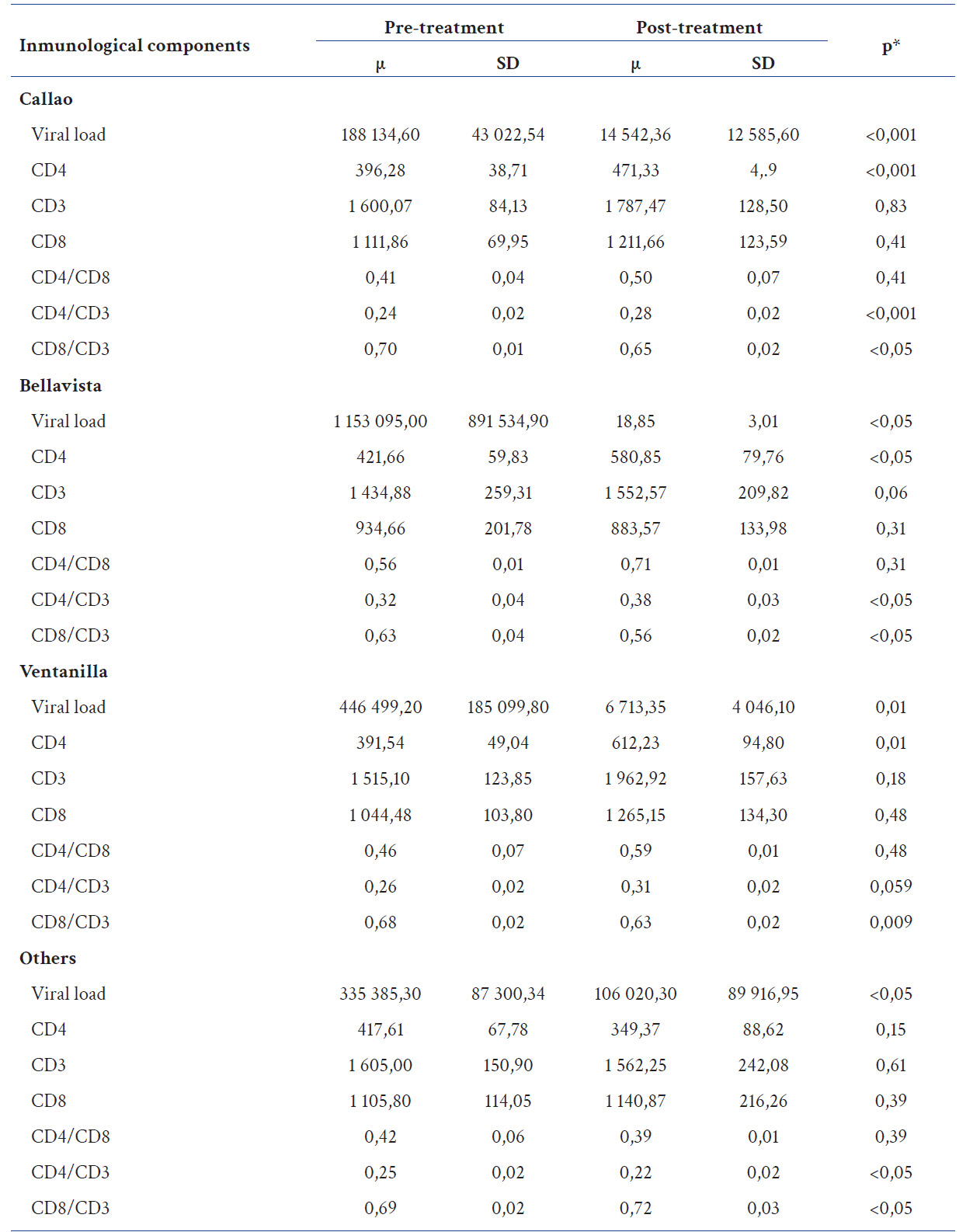
Data obtained was reported as means ± standard deviation. The statistical package STATA v. 17.0 (StataCorp, CollegeStation TX, institutional license for Universidad Peruana Cayetano Heredia) was used. To evaluate the difference between means, immunological components before and after treatment, the student’s t-test for paired samples was used. The areas of the Callao region were divided into districts with the largest population and/or extension, such as Callao, Bellavista and Ventanilla, the rest of the population was taken together in a fourth category. A p<0.05 was considered as statistically significant.
RESULTS
During the period 2021-2022, a total of 289 patients were evaluated for HIV infection at the Laboratorio de Referencia Regional de Infecciones de Transmisión Sexual y Metaxénicas, of which 207 (71,62%) were men. The average age was 32,26 years. The most frequent population at risk was MSM with 21,8% and 5,88% were inmates (table 1).
Table 1 Description of the study sample.
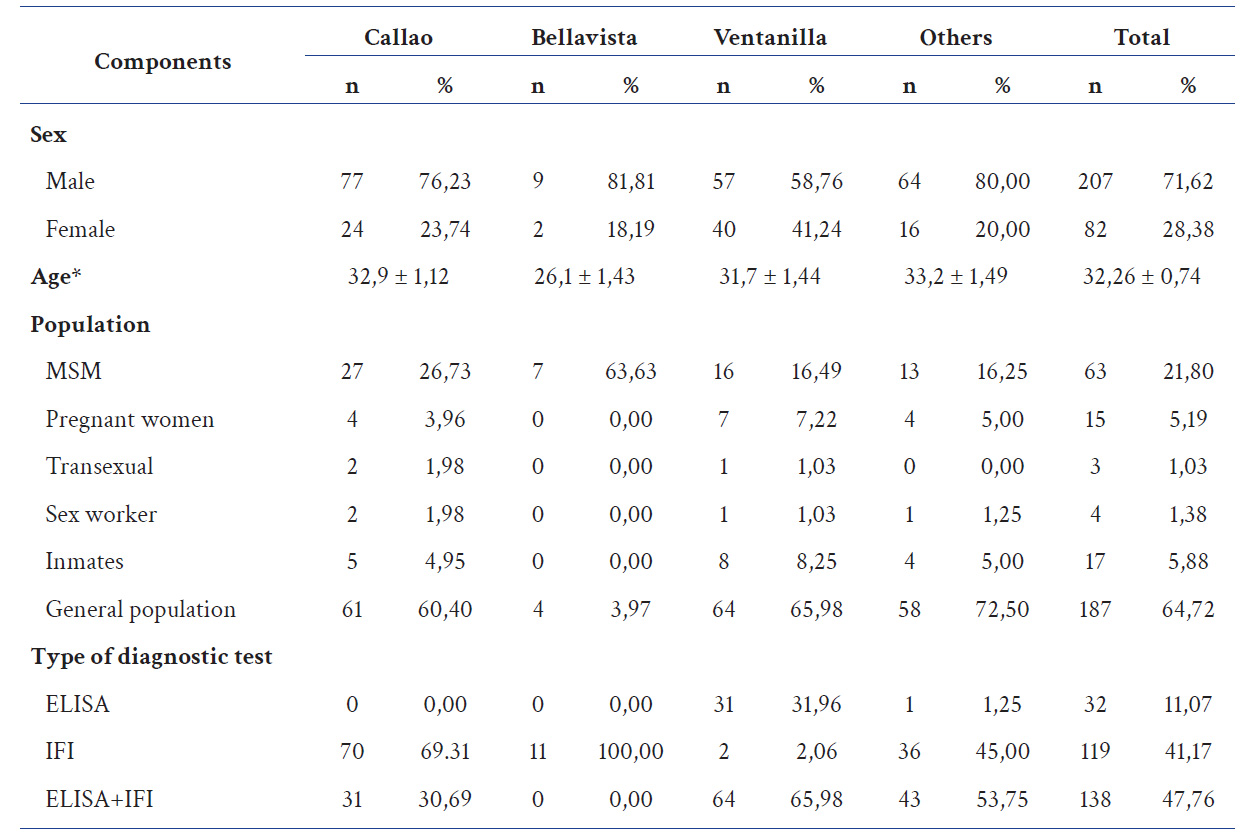
*Mean and standard deviation are displayed
MSM: Men that have sex with other men.
In table 2 can be observed that people who received Antiretroviral Therapy-ART, had a statistically significant decrease in the Viral Load values and an increase in CD4+ levels (p<0,05).
DISCUSSION
Our results show a mixed picture for treatment-compliant patients, observing a significant difference between viral load and CD4 count in the different districts of the Callao region. These results frame the need for timely diagnosis and treatment of HIV.
In a previous research, Ochodo et al. 5 proved that the use of point of care for viral load has high sensitivity and specificity for the diagnosis of HIV-1 in patients attending health centers at a clinical threshold of ≥1 000 copies/ml, furthermore Ochodo et al. 6 in another investigation were able to diagnose HIV-1/HIV-2 infection by NAT (Nucleic Acid Test) methodology in infants and children under 18 months, showing high sensitivity and specificity, except those who were previously exposed to HIV infection.
Within the confirmatory diagnosis, the Cepheid Xpert HIV-1 platform has high concordance and accuracy as a method of testing for HIV RNA Viral Load, concluding that the use of the Cepheid Xpert HIV-1 diagnostic platform is a promising tool for monitoring patients on Antiretroviral Therapy-ART 7. In Callao this technology is used, guaranteeing an adequate follow-up of the target population.
In a study conducted in several countries that managed to implement the 2013 WHO recommendations on "test and treat", concluded that youth and adolescent-friendly programs are needed to achieve access and adherence to treatment 8. Also, a great strength is the use of data at the regional level, since it is highly representative and allows us to evaluate the strategies applied to conditions or diseases that have an impact on public health, as has been seen in other studies 9. There has been a successful implementation of HIV surveillance and control plan in Callao, evidenced by the lower levels of viral load in the follow-up consultations of the patients.
Finally, it is important as a health strategy to follow-up confirmed patients and at-risk populations so that indicators are met and public health in the region are stabilized.