Servicios Personalizados
Revista
Articulo
Indicadores
-
 Citado por SciELO
Citado por SciELO
Links relacionados
-
 Similares en
SciELO
Similares en
SciELO
Compartir
Industrial Data
versión impresa ISSN 1560-9146versión On-line ISSN 1810-9993
Ind. data vol.24 no.1 Lima ene./jun 2021
http://dx.doi.org/10.15381/idata.v24i1.16287
Production and Management
Competency-Based Management for Organizational Development at Universidad Nacional Mayor de San Marcos
1 Degree in Business Management from Universidad Inca Garcilaso de la Vega. Currently working as head of Marketing at the Centro de Informática of the Universidad Nacional Mayor de San Marcos. (Lima, Peru). E-mail: lcastilloa1@unmsm.edu.pe
This study aims to contribute to the improvement of human resources management through a competency-based management model for administrative positions in the central administration that will lead to organizational development at Universidad Nacional Mayor de San Marcos. This is because, on some occasions, people who hold administrative positions lack the training required to manage, and only have technical knowledge, which is not enough to achieve the objectives determined in university’s strategic plan. Different bibliographic sources, studies related to the topic, as well as the methodology established by SERVIR were reviewed. The study revealed that no specific measures have been established for the profiles of management positions at the university, so that it is therefore necessary for the human resources office to implement a competency-based management model and enforce the established guidelines. The introduction of a new proposal based on the competencies to the university invites us to redesign the work profiles in terms of performance functions.
Key words: human talent; competencies; management; university
INTRODUCTION
At present, public and private universities are using new competency-based management models for human resources to introduce competitive tactics to address global changes and meet the needs of the human intellect. Accordingly, the general objective of this research is to improve human resources management based on competencies to enable organizational development within the university. For this purpose, it is essential to review various bibliographical sources, studies on the subject and the guidelines of the Autoridad Nacional del Servicio Civil (SERVIR) as the governing body of public servants.
This research proposes a study on human resources management in public and private universities based on competencies, using a model that details the competency-based performance profiles for administrative positions that may be used in future research. It further proposes to establish a competency-based management system for the institutional environment of the university that contributes to the elaboration of the position profiles in order to increase administrative productivity.
Peruvian universities have gone through various organizational changes over the years, and it has been observed that decision-makers react to different situations when they occur, rather than anticipating them, triggering political disruptions and/or interventions that result in the instability of organizational climate. Most often, people in management positions lack the necessary managerial skills, but are hired for their academic and/or technical knowledge, which are insufficient to lead teams and make decisions. The way in which university managers perform their functions is directly related to organizational development (OD), hence the importance of ensuring that the members are satisfied with the performance of their functions so that, as a team, they achieve success and institutional objectives. The main function of administrative positions within the public university is the efficient management of its own or ordinary resources.
BACKGROUND
According to Delgado (2002), proper administration consists of effectively and efficiently using the university’s resources, namely, all the members of a university, in order to achieve the institution’s objectives. Those who manage the university should have an idea about the members of this community. A new form of managing a university should be based on a management team that works with responsibility, diligence and efficiency.
Thus, for proper management, human resources departments should consider using competency standards, as having the most suitable personnel will ensure compliance with institutional objectives as part of organizational development. In addition, an individual’s skills to perform the job functions are identified through the achievement of objectives.
From the various bibliographic sources reviewed, it was found that competency-based management is a management prototype that aligns human capital with the essence of the organization, so that workers are professionally oriented, which contributes to the fulfillment/ of the strategic plan.
In this regard, several studies have addressed human resources management in universities. According to one, a competency-based management model should be implemented for the administrative profiles of a university, because a) a competency-based approach supports continuous learning, helps to incorporate training programs and to adapt to the technological advances; b) it specifies the profile of suitable personnel and thus provides an understanding of what is expected of the administrative-teaching staff and how competencies efficiently help in achieving the objective; c) personnel selection should no longer be based solely on academic degrees, but also on the competencies that the personnel suitable for the job profile should have; and d) it allows updating administrative profiles in order to align development plans to the needs of each area (Rodríguez, 2015).
In organizations, human talent management consists of recognizing the value of employees, improving their productivity and retaining them, because they are essential elements for the efficient management of the organization; human capital management is a perceptible factor in organizational culture, especially considering that individuals spend most of their lives working, and organizations depend on them to operate and achieve their objectives (Chiavenato, 2002).
In Human Capital, Becker (1964) focused on the study of information societies, and determined human beings to be the most valuable capital for organizations, on account of their knowledge and skills manifested in their work habits. Thus, Becker considers human talent as the main factor for the performance of today’s economies, since human productivity is based on knowledge.
Alles (2008) explains that current business management models promote the development of employees depending on the organization’s strategic plans, therefore, all members of the organization can be involved in the organizational strategy and participate in its execution, which leads to the fulfillment of the objectives set.
In Testing for Competence Rather Than for “Intelligence”, McClelland (1973) defines the term “competence” as the main trait of human beings, as it is the source of their productivity for the performance of their functions at work.
On the other hand, Spencer and Spencer (1993) define competencies as the main attributes of human beings, which are manifested in their behavior or mindset.
A comprehensive concept of competency-based management suggests that it is a perennial means of integration where the organization incorporates the needs and desires of workers in order to help and support them so that they continue to contribute to the institutional objectives. According to Fernández (2006), human talent management involves the development of new proposals to simplify management of workers and their adaptation to the needs of the company.
Competency-based management represents not only the future, but also the current need for a new workforce generation in organizations. It will identify the main competencies that a person requires to meet the profile of a position, which will allow to maintain high or superior performance levels and incorporate the ideal individual into the organization, which in turn will create competitive advantages for the organization’s development.
Several authors have made contributions about OD, which is understood as an administrative tactic that enables the fulfillment of the strategic plan through the proper use of management and human resources tools. De la Cruz (1999) describes organizational development as a procedure that takes into account all the elements related to change in order to develop a new organizational model, focusing exclusively on the human factor.
Organizational development should focus on establishing the mission, vision, institutional values, tactics and their implementation, to ensure that all employees are able to adapt to continuous change.
Sánchez (2009) states that a proper administrative process, together with the evaluation of personnel performance, achieves the success of the competitive strategy, adding to the premise: human capital and its aspiration to achieve objectives pushes finances and technology into the background.
The classic author on organizational development, Bennis (1997, as cited in Sánchez, 2009), explains that it is a response to change, a complex educational strategy that aims to change management attitudes in the organization and restructure it so that it can adapt to global changes in organizational trends, such as new technologies, markets and business challenges.
Chiavenato (2006) states that OD is a long-term procedure, led by the general management of the organization, that allows the organization's processes to be more effective and contributes to personnel development.
Based on the definitions of OD, the nexus between organizational development and university management can be reshaped into organizational processes, including their theoretical, methodological and operational characteristics, which allow the achievement of institutional objectives.
According to Espinoza (2000):
Hoy en día, la premisa “capacidad gerencial demostrada” en la gerencia universitaria no es un elemento valorativo para componer la estructura gerencial de la universidad, queriendo significar que el personal que ocupa cargos de gestión muchas veces están ahí por cuestiones políticas y/o de poder político. [At present, the premise “demonstrated managerial competence” in university management is not considered an important element in the constitution of the university’s management structure, thus implying that the personnel in management positions are often there on account of political interests and/or political power.] (p. 87)
In the opinion of Fernández (2008):
La Universidad es un centro generador de conocimiento, y por ello su rol y efecto en el desarrollo de las sociedades y de los países es fundamental. Sin embargo, principalmente en el caso de la universidad pública, existen varios factores que impiden su mayor competitividad y liderazgo; y por lo tanto su aporte en el desarrollo del país. Un factor podría ser la forma de gobierno o gestión universitaria; otra sería su cultura y/o medioambiente organizacional. La Universidad pública peruana presenta diversos problemas que suceden en un entorno interno y externo adversos. Internamente, puede estar la falta de una gestión universitaria que defina e implemente estrategias para la competitividad y calidad; y externamente, el rol del Estado, por su falta de intervención y definición de una política educativa como estrategia de desarrollo y bienestar. [Universities are sources of knowledge, and therefore their role and impact on the development of societies and countries is paramount. Nevertheless, mostly in public universities, several factors interfere with their competitiveness and leadership, and consequently hinder their contribution to the country's development. These factors could be the university governance or management and its organizational culture and/or environment. Public universities in Peru face a number of problems in an adverse internal and external environment. Internally, there is the lack of a university management that defines and implements strategies for competitiveness and quality; and externally, the role of the State, for its lack of intervention and definition of an educational policy as a strategy for development and welfare.] (p. 3)
The Universidad Nacional Mayor de San Marcos (UNMSM) is an educational entity aimed at perfection and leadership. As such, people involved in its management must comply with the corporate objectives and be resourceful when faced with the constant changes that university management demands. Committed and identified personnel with high levels of competence are required to achieve a stable and continuous organizational development; likewise, it is necessary to provide service quality and promote the achievement of strategic objectives. Therefore, training for administrative positions must be arranged for the improvement of knowledge.
The Reglamento de Organización y Funciones (ROF) approved with R.R. No. 01206-R-11 (2011) is the official document that recognizes the UNMSM as an educational institution, details its nature and authority, and the general and specific functions of each of its bodies and its administrative units.
In Peru, the management and administrative staff of public educational institutions work based on SERVIR’s guidelines, complying with training and continuous development regimes for public servants. This research used the guidelines of the Manual de Perfiles de Puestos [Position Profile Manual] (MPP), approved with Directive No. 001-2016-SERVIR/GDSRH (2016).
METHODOLOGY
This is a mixed study, qualitative because the information collected expresses quality, and quantitative because information was collected using indicators; data analysis was performed using statistical programs. Its nature is descriptive-correlational, as it aims to measure the relationship between competency-based management and organizational development at the university; and it follows a non-experimental design. Respondents’ opinions were also examined based on their answers and observations and thus it was possible to know their concept of competency-based management, which provided an idea of how to optimize OD using the results in favor of managerial competencies.
Based on data from the 2016 statistical compendium, the study population was selected from central management. From a total of 1275 administrative staff, including authorities, directors, heads and workers, a representative sample of 296 was selected. The stratified probability sampling method and information from secondary sources were used to select the sample.
RESULTS
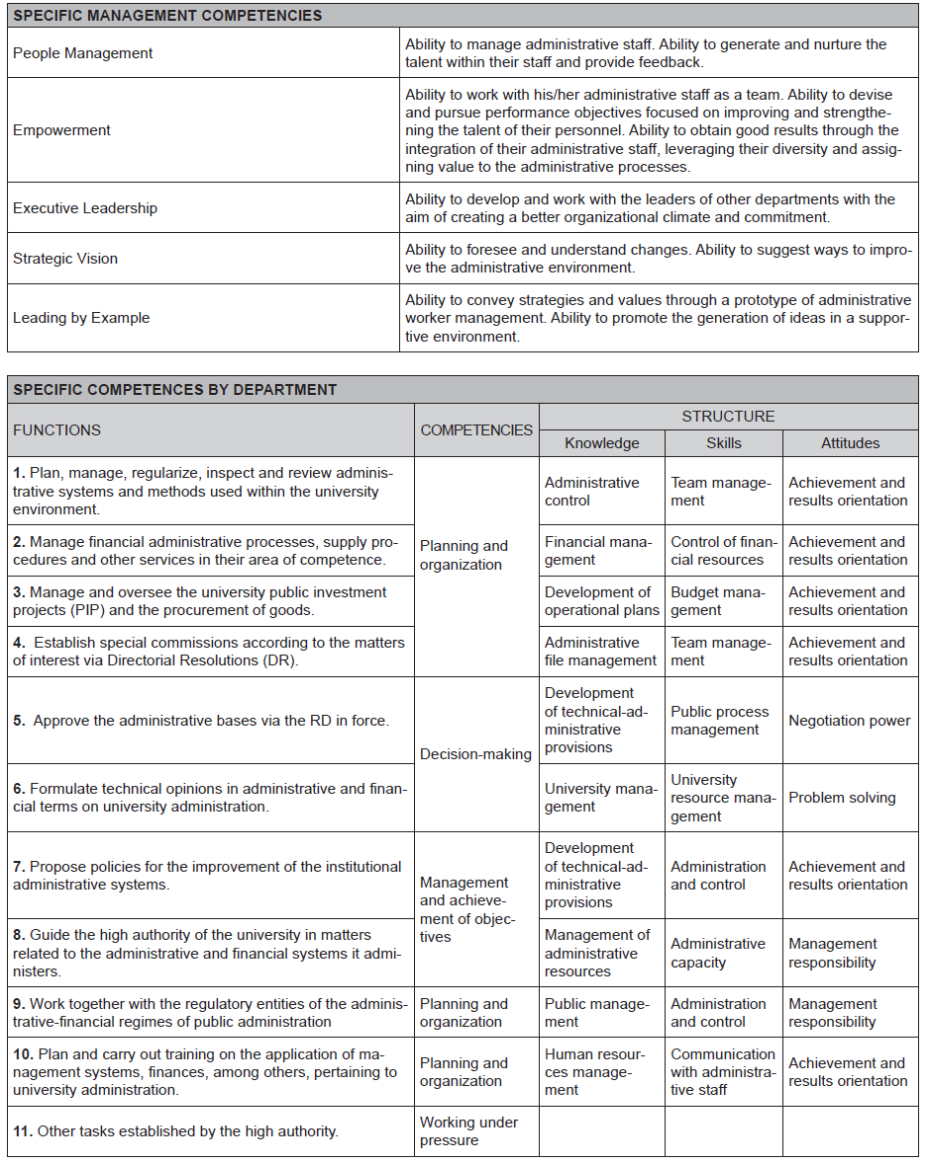
A Likert scale questionnaire was used as data collection technique, and it was applied to administrative personnel in order to gather their opinions on management competencies. Five specific management competencies from the book by Alles (2009) were included in the questionnaire:
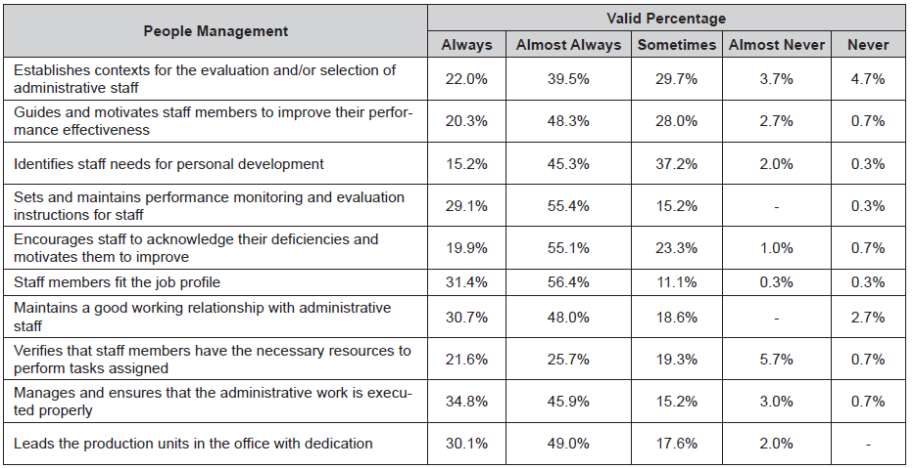
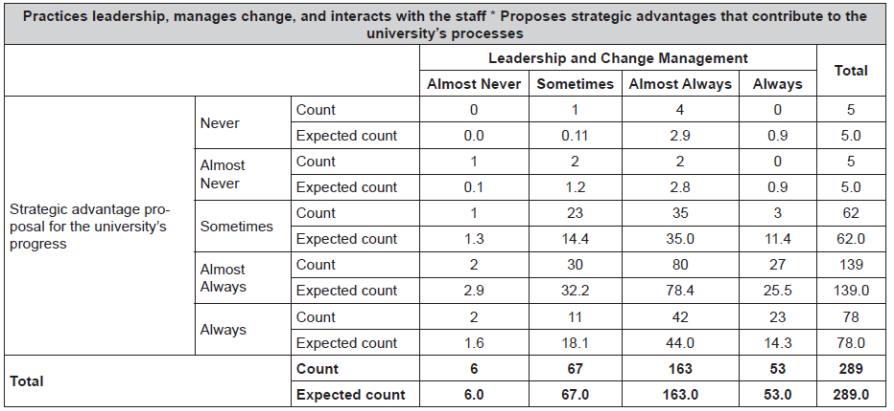
People Management. This is the ability to assess and select the personnel working at the university. The results obtained from the questionnaire are shown in Table 1.
As shown in Table 1, 56.4% of the respondents state that the necessary actions for good personnel management are “almost always” undertaken.
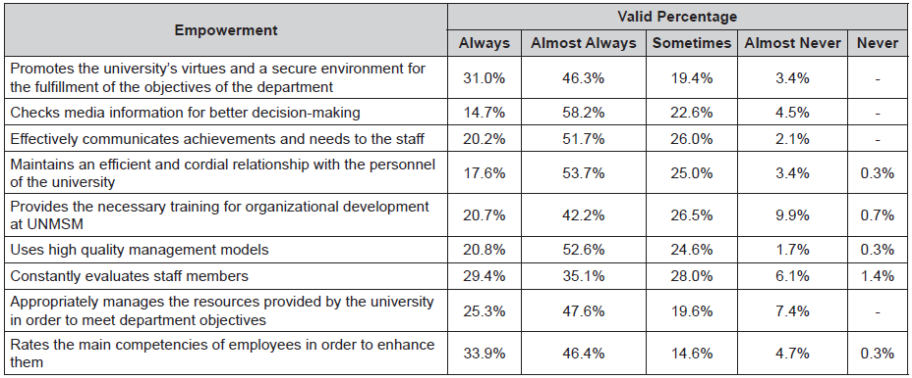
Empowerment. It is the ability to achieve UNMSM’s goals through holistic work management and development of values based on appropriate communication between information channels to make better decisions. The results obtained from the questionnaire are shown in Table 2.
As shown in Table 2, 58.2% of the respondents state that the necessary actions for managing teamwork, through appropriate communication between information channels, are “almost always” undertaken.
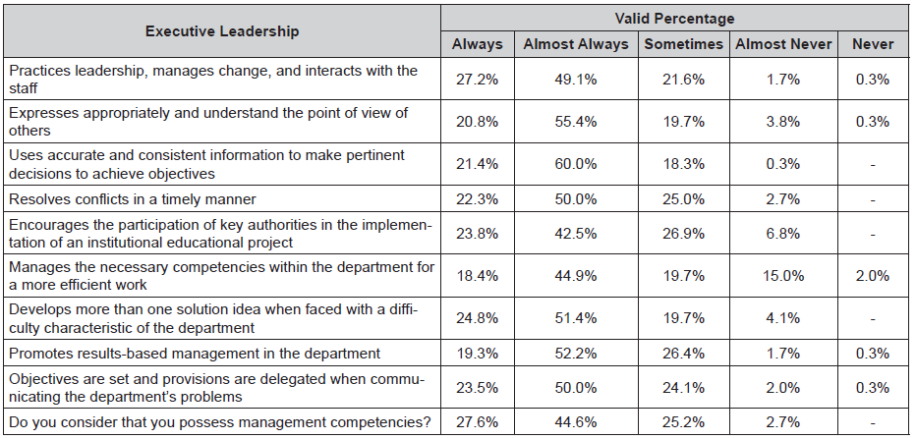
Executive Leadership. It comprises the main functions of UNMSM’s management team for the implementation of strategic changes, team leadership and adequate conflict management. The results obtained from the questionnaire are shown in Table 3.
As shown in Table 3, 60% of the respondents state that the necessary actions to motivate work teams, carry out strategic changes and manage conflict management are “almost always” undertaken.
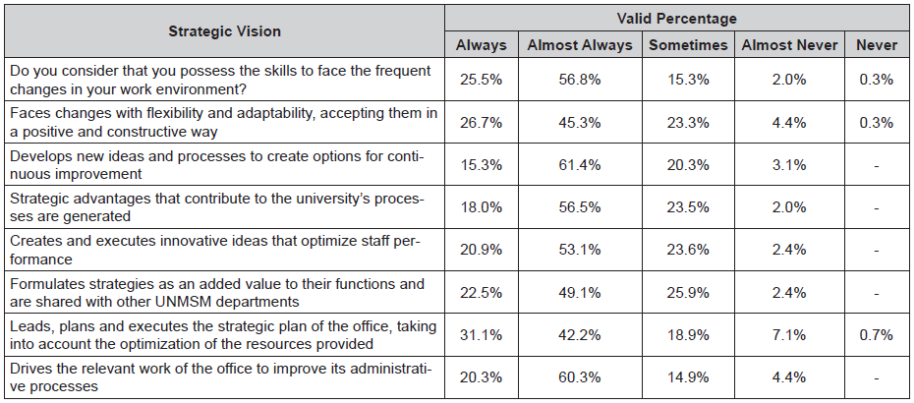
Strategic Vision. It is the ability to adjust to the changing educational environment, create administrative alliances between the different departments at UNMSM in order to contribute to the fulfillment of the determined strategic objectives. The results obtained according to the questionnaire are shown in Table 4.
As shown in Table 4, 61.4% of the respondents state that the necessary actions to keep abreast of changes in the educational context are “almost always” undertaken.
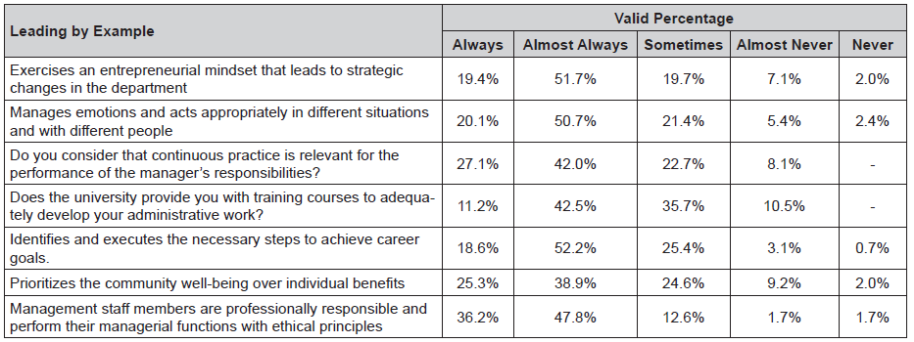
Leading by example. It is the emotional control of the manager and/or boss to motivate changes in his or her department and to be an example for the personnel. The results obtained according to the questionnaire is shown in Table 5.
As shown in Table 5, 52.2% of the respondents state that the necessary actions to manage the administrative position in terms of emotional control and encouraging changes in the department are “almost always” undertaken.
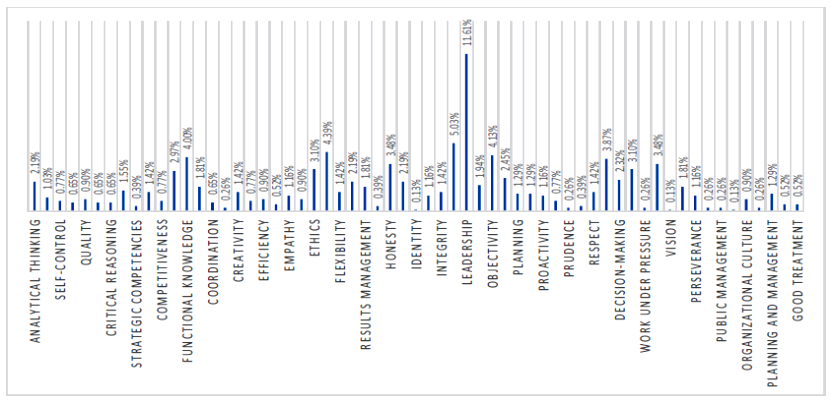
To learn about the competencies considered at UNMSM, the following question was asked: What main competencies should a manager have in order to hold a university management position? The results obtained from the questionnaire are shown in Figure 1.
A list of the competencies that, according to the respondents, their superiors should possess to better perform their functions is shown in Figure 1. Leadership is the competency that stands out the most with 11.61%.
Upon analyzing the information, certain deficiencies and problems were identified that need to be addressed in collaboration with the administrative staff. It is advisable to develop a competency-based human talent management model that contributes to the performance of administrative leaders in order to optimize the quality and efficiency of administrative processes. Hence the importance of setting specific competencies per position through a functional analysis of each profile that allows determining the proper competencies.
Hypothesis Testing
According to Hernández et al. (2010), hypotheses state what we intend to demonstrate, so that they are defined as possible explanations of the phenomenon under study. They should be formulated in the form of a proposition.
General Hypothesis
H 1 : There is a relationship between competency-based human talent management and organizational development at UNMSM.
H 0 : There is no relationship between competency-based human talent management and organizational development at UNMSM.
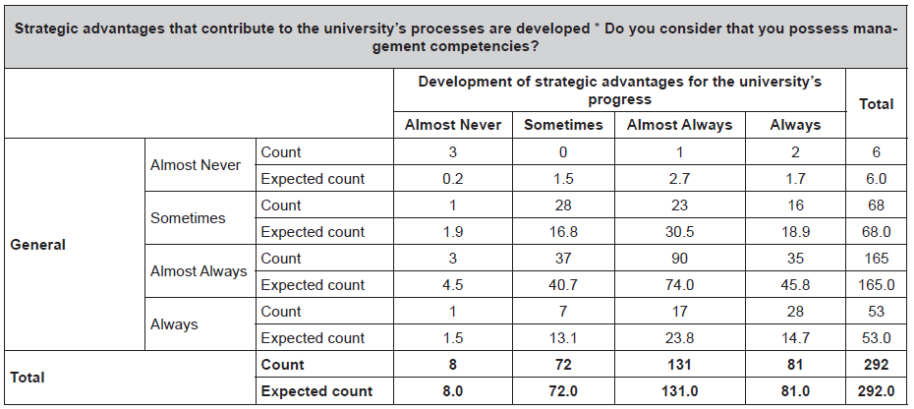
Data presented in Tables 6 and 7 support the hypothesis.
Table 7 Chi-Square Test-General Hypothesis.
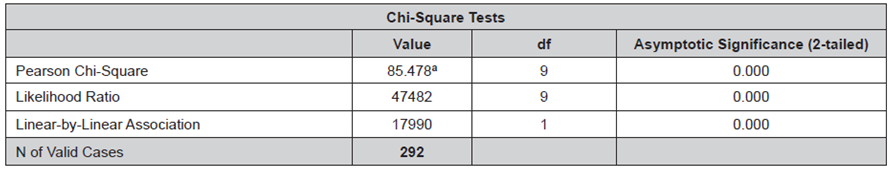
a. 7 cells (43.8%) have expected count less than 5. The minimum expected count is 0.16.
Source: Prepared by the author.
The significance level is 0.000 < 0.05, therefore the null hypothesisH 0 is rejected andH 1 is accepted.
Specific Hypothesis 1
H 1 :There is a correlation between the development of competency-based management and competitiveness at UNMSM.
H 0 :There is no correlation between the development of competency-based management and competitiveness at UNMSM.
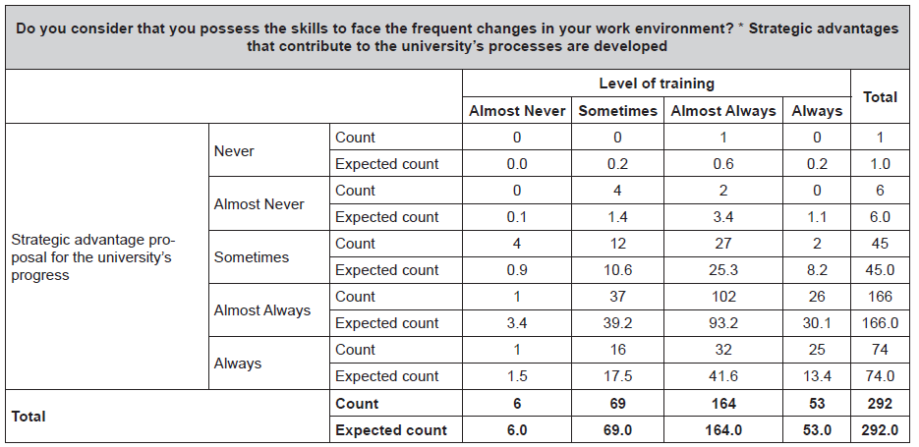
Data presented in Tables 8 and 9 support the hypothesis.
Table 9 Chi-Square Test - Specific Hypothesis1.
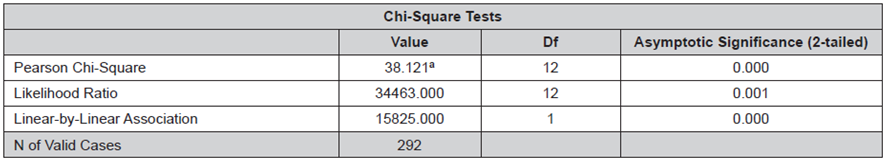
a. 11 cells (55.0%) have expected count less than 5. The minimum expected count is 0.02.
Source: Prepared by the author.
The significance level is 0.000 < 0.05, therefore the null hypothesisH 0 is rejected andH 1 is accepted.
Specific Hypothesis 2
H 1 :There is a correlation between the competency-based management system and the improvement of position profiles at UNMSM.
H 0 :There is no correlation between the competency-based management system and the improvement of position profiles at UNMSM.
Data presented in Tables 10 and 11 support the hypothesis.
Table 11 Chi-Square Test - Specific Hypothesis 2.
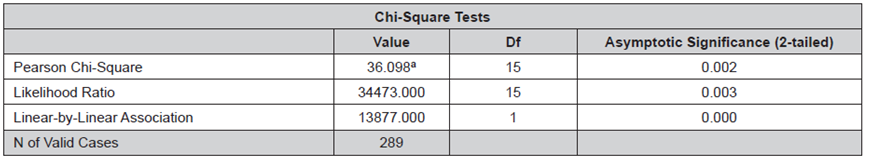
a. 15 cells (62.5%) have expected count less than 5. The minimum expected count is 0.02.
Source: Prepared by the author.
The significance value is 0.002 < 0.05, therefore, the null hypothesis H0is rejected and H1is accepted.
DISCUSSION
Following the analysis of the information collected, it was found that competency-based management and organizational development are related. Some deficiencies and problems that require a solution were also found among the administrative employees at the university's headquarters; it is therefore necessary to introduce a competency-based management model in the area of human resources management so that people in administrative positions may improve their performance. The selection of human talent is an action aimed at finding the person who possesses the competencies, knowledge and other elements, such as academic degrees, necessary to obtain a specific job position within an organization.
As for the selection process used by the university, certain instruments were designed to efficiently supply suitable personnel. In addition, each department's management team attempts to establish stimulation and alignment processes in order to constantly improve the performance of its functions. In addressing these needs, the administrative staff attempts to maintain organizational development within the central administration.
It is essential that the human resources general office expedite the process of implementing the SERVIR guidelines for the application of the Position Profile Manual by management competencies in administrative positions. Also, considering each of the indicators assessed in this study, it can be stated that there are some situations to which more attention should be paid in order to raise the observations, despite the fact that the activities determined by position are being carried out.
A competency-based job profile design proposal was developed from the data analysis to contribute to the general objective (see Appendix 1). It sets out the occupations and competencies necessary for the adequate development of functions. It also contributes to the improvement of SERVIR forms at the university via the inclusion of fundamental competencies, the improvement of the level of development for the performance of functions, the adjustment of personnel to the job position, the introduction of a dictionary of managerial competencies and the adequate description of the job profile.
The use of a competency-based management guide within universities would benefit organizational development as stated by Rodríguez (2015):
Mejora la precisión para determinar el nivel de ajuste y potencial de una persona para diferentes trabajos, de tal forma que los planes de desarrollo puedan relacionarse mejor con las áreas donde realmente se necesita, tal como se puede corroborar en los estudios que sobre la materia ha desarrolladoAlles (2009), en los que da cuenta de la importancia de los programas de desarrollo de las personas bajo el modelo de competencias y su relevancia para el crecimiento y continuidad de las organizaciones. [It improves the accuracy to determine a person’s potential and level of adjustment to different jobs, so that development plans may be better related to the areas where they are really needed, as can be verified in the studies conducted by Alles (2009), in which the importance of people development programs following the competency model and its relevance for the growth and continuity of organizations is explained.] (p. 358)
Performance evaluation processes for administrative positions must also be considered in order to monitor employees’ development and use that information to develop training programs. For organizations to remain at the forefront, they must update their processes and adopt new approaches that favor the development of employees’ functions, in order to optimize resources and foster proper organizational development.
CONCLUSIONS
Competency-based management and organizational development are correlated; therefore, the role of the human resources department at the university is essential to recruit the best talent for administrative positions, based on competency-based management that influences organizational development.
Low levels of support regarding the needs of personnel are observed. Evidence of this can be found in the item of perceived support for employees’ development within the university, where 32.6% stated that no adequate support was provided to perform their functions satisfactorily.
No specific measures have been established by the university regarding personnel selection formats that include the concept of competencies for each job profile.
RECOMMENDATIONS
It is essential to devise tools to measure the competencies established during the development of the tasks and thus be able to implement the processes required to enhance management competencies. Greater competitiveness should be pursued in the fulfillment of objectives and the institutional mission in order to achieve academic success.
A document describing and specifying the essential functions and responsibilities of the position profile, including a competency assessment, should be prepared.
Training budgets should be used to prepare the management team members for the efficient and effective performance of their functions. Furthermore, their performance should be assessed in a collaborative fashion.
REFERENCES
[1]. Alles, M. (2008).Dirección Estratégica de Recursos Humanos Gestión por Competencias. Buenos Aires, Argentina: Ediciones Granica S.A. [ Links ]
[2]. Alles, M. (2009).Diccionario de competencias: La trilogía. Las 60 competencias más utilizadas. Buenos Aires, Argentina: Ediciones Granica S.A. [ Links ]
[3]. Becker, G. (1964).Human Capital. Nueva York, Estados Unidos: Columbia University. [ Links ]
[4]. Chiavenato, I. (2002).Gestión del Talento Humano(2ª ed.). Santafé de Bogotá, Colombia: McGraw Hill. [ Links ]
[5]. Chiavenato, I. (2006).Introducción a la Teoría General de la Administración(7ª ed.). México D.F., México: McGraw Hill. [ Links ]
[6]. De la Cruz, G. (1999). Problemas y principios para el desarrollo de las organizaciones modernas.Gestión en el Tercer Milenio, 2(3), 45-54. [ Links ]
[7]. Delgado, L. (2002). La Gestión Universitaria. En C. Aljovín y C. Germaná(Eds.),La Universidad en el Perú(págs. 81-88). Lima, Perú: Fondo Editorial UNMSM. [ Links ]
[8]. Directiva N° 001-2016-SERVIR/GDSRH. Normas para la Gestión del Proceso de Diseño de Puestos y Formulación del Manual de Perfiles de Puesto - MPP. Diario Oficial El Peruano (2016). [ Links ]
[9]. Espinoza N. (2000).Gerencia Universitaria: Universidad peruana y tercer milenio. Perú, Lima: Editorial San Marcos. [ Links ]
[10]. Fernández L. (2008).Análisis de la gestión universitaria en la universidad pública peruana[artículo]. VIII Coloquio Internacional sobre Gestión Universitaria en América del Sur, Asunción, Paraguay. [ Links ]
[11]. Fernández J. (2006).Gestión por competencias. Madrid, España: Pearson Educación S.A. [ Links ]
[12]. Hernández R., Fernández C., y Baptista P. (2010).Metodología de la Investigación .Bogotá, Colombia: McGraw Hill. [ Links ]
[13]. McClelland, D. (1973). Testing for Competence Rather Than for “Intelligence”.American Psychologist, 28(1), 1-14. [ Links ]
[14]. Resolución Rectoral N° 01206-R-11. Reglamento de Organizaciones y Funciones de la Universidad Nacional Mayor de San Marcos (2011). [ Links ]
[15]. Rodríguez, J. (2015). Implementación del modelo de gestión de talento humano por competencias en una universidad de Lima Metropolitana.Propósitos y Representaciones, 3(2), 319-401 [ Links ]
[16]. Sánchez, G. (2009). El Desarrollo Organizacional: Una Estrategia de Cambio para las Instituciones Documentales. Anales de Documentación , ( 12 ),235-254. ISSN: 1575-2437. [ Links ]
[17]. Spencer L., y Spencer S. (1993). Competence at work: Models for Superior Performance. Nueva York, Estados Unidos: Wiley & Sons. [ Links ]
Received: June 17, 2019; Accepted: February 25, 2021











 texto en
texto en