Introducción
Problem behavior is defined as behaviors that do not comply with cultural norms in terms of intensity, frequency and duration, which are dangerous for the individual and the environment and seriously prevent the individual from reaching the social areas (Sucuoglu & Demir, 2017; Castillo et al., 2018). Today, problem behaviors are very common in children with typical developmental and developmental delays (Erbas, 2005). Children who exhibit problem behavior experience many problems in the academic, social and familial areas that are expected to function appropriately for their age and need support in this regard. The fact that problem behaviors can last for a lifetime without any intervention necessitated the development and effective use of evidence-based programs and the need for support of children (Chandler & Dahlquist, 2002; Sugai & Horner, 2008; Ceylan &Yikmis, 2017; Atbasi, Karasu & Tavil, 2019).
One of the evidence-based programs developed for problem behavior is positive behavior support (PBS). Positive behavior support emerged in the mid-1980s as an approach to understanding and dealing with problem behaviors and was developed by using Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) (Dunlap et al., 2008; Doll, 2019). A relevant aspect of PBS implementation is the adoption and integration of behavioral and non-behavioral approaches, both in theoretical perspectives and in evidence-based practices (Childs et al., 2015). In this context, PBS can be regarded as a framework for organizing the delivery of active service supports in accordance with a set of basic principles. Adopting a framework approach explains the value of years of research and professional practice development in various disciplines in health and social care, such as psychiatry, psychology, social work, nursing, speech and language therapy, occupational and physiotherapy. In addition, Case-Smith and Arbesman (2008) stated that there is a whole set of research and practice that helps us understand how we can effectively work with organizations and systems within organizations, with clear results of interdisciplinary colleagues relationships for the intervention of problem behaviors.
PBS is a practical approach for individuals of all ages and abilities to reduce problem behaviors and improve quality of life and focuses on meeting the needs of a person in critical areas of life such as family, living, financial, educational / professional, social / recreational, behavioral / emotional, psychological, health, legal, cultural and security(Crone, Hawken & Horner, 2015). Bradshaw, Mitchell and Leaf (2010) revealed that PBS aims to increase quality of life of the individuals, help the individual achieve his / her goals in a socially acceptable way, make the problem behavior as insignificant, ineffective and ineffective, thereby reduce or eliminate all parts of the problem behavior. PBS interventions are also found to be effective for individuals with giftedness, autism spectrum disorder, developmental delay and typical development (Erbas, 2005; Blair et al., 2011; Citil, 2016; Halder, 2019).
The key element in PBS education is to train people about internal and external factors that contribute to coercive behaviors, reduce problem behaviors and present an alternative functional behavior instead of the problem behavior. Basic characteristics of a PBS program are:
changes in lifestyle and quality of life;
continue for a life time;
environmental validity;
multiple applications;
emphasis on practices to prevent problem behavior (Lucyshyn, Dunlap & Albin, 2002; Erbas, 2008).
PBS is a therapeutic program that can be applied by professionals from various disciplines depending on the problem areas they live in, for individuals of all ages and abilities. When the literature is examined, it is seen that number of studies providing an evaluation on the studies of PBS is limited. Therefore, it is considered that this study would provide an overview on the trends in the studies on PBS for researchers and professionals working in this field. Considering the positive outcomes of PBS for reducing problem behavior and the importance of providing a review for studies on PBS,the aim of this study is to focus on the topic of positive behavior support and show the contribution of the studies on PBS to the field. In line with this general aim, answers to the following questions were sought in the study:
What is the distribution of the studies on PBS according to year of publication?
What is the distribution of the studies on PBS according to year and country?
What is the distribution of the studies on PBS according to published journal and subjects?
What is the distribution of the studies on PBS according to subject, year and country?
What is the distribution of the studies on PBS according to research sample?
What is the distribution of the studies on PBS according to data collection tools?
What is the distribution of the studies on PBS according to type of documents and year?
What is the distribution of the studies on PBS according to research method and year?
What is the distribution of the studies on PBS according to subject and research method?
What is the distribution of the studies on PBS according to data analysis method?
What is the distribution of the studies on PBS according to sample size? What is the distribution of the studies on PBS according to authors’ study interests?
Method
Research Model
In this study, "positive behavioral support" was searched in Scopus database and 168 articles in English were reached. The articles were reviewed individually and a total number of 77 articles that involved" positive behavior support" in the title of the published documents were included in the study and 91 articles that did not meet this criterion were excluded from the study. Of the 77 articles included in the study, 24 could not be reached because they were open-access, and as a result, 53 articles that focused on "positive behavior support"were included in the study and evaluated by the content analysis method. Content analysis is a research technique used to draw systematic and objective results from certain characters defined in the text (Kocak &Arun, 2006) and this research method has been chosen because of its suitability for the aims of the present study.
Population and Sample
The population of this study consists of 168 articles on "positive behavior support"published in journals within Scopus database. The research sample was composed of 53 articles published in 35 different journals, focusing on positive behavior support published between 1998 and 2019 (May). There is no limitation according to the publication year of the manuscript and all researches that meet other criteria in the database are included in the study.
Data Collection Tool
A coding form was created and used by the researchers including the year of publication, name of the journal, country in which the research was conducted, research subject, research sample, sample size, authors’ research interests, research method, data collection tool and data analysis method, type of document.
Data Analysis
In this study, content analysis technique was used to evaluate the data obtained.Categories were formed after content analysis. In order to find out frequency and percentages, categorized data were entered into SPSS program and analyzed.
Reliability and Validity
The data obtained from the study were collected by a researcher by examining the articles one by one and processing them into the coding form. At the end of the process, the collected data were subjected to a second control by the other researcher. The researchers then divided the data into specific categories for entry into SPSS program, mutually checked and agreed. In this way, it was tried to provide validity and reliability by performing double checks
Results
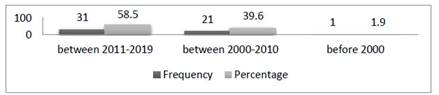
Distribution of articles on positive behavior support by year of publication Figure 1 shows the distribution of articles on PBS by year of publication. While only one (1.9%) of the 53 articles examined within the scope of the research was written in 1998, there were 21 articles (39.6%) written between 2000 and 2010 and 31 articles between 2011-2019. This reveals that the subject matter has become more important from the past to the present.
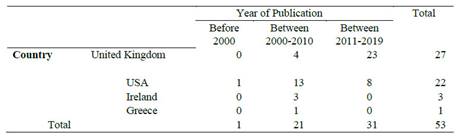
Distribution of the countries of the articles on positive behavior support by year of publication Table 1 shows the distribution of the countries of the articles on positive behavior support by year of publication. Positive behavioral support was found to be the most commonly addressed by researchers in the United Kingdom with 50.9%, followed by the United States with 41.5%. Apart from these two countries, it was found that there were 3 articles from Ireland and 1 article from Greece and these 4 articles were written between 2000-2010. In other words, it is seen that this subject, which has been given more importance and examined especially between 2011-2019, has become a much more studied subject in the UK.
Distribution of articles on positive behavior support by subject of the journals
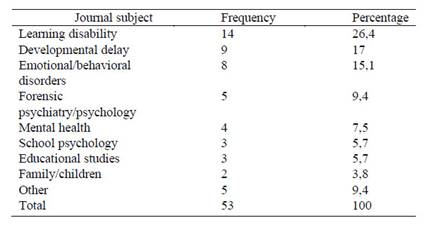
Within the scope of the research, articles published in 35 different journals were examined and among these journals, the 13 articles which is the highest frequency were published in Tizard Learning Disability Review. The journals in which articles on PBS are published are categorized according to their subjects and Table 2 shows the distribution of the articles according to the subjects they focus on. The articles were published in a journal focused on learning disability with 26.4%, developmental delay with 17%, emotional / behavioral problems with 15.1%, forensic psychiatry / psychology with 9.4%, mental health with 7.5%. Results also showed that there are journals focusing on school psychology (5.7%), educational studies (5.7%), children / family (3.8%).
Distribution of articles on positive behavior support by research topic
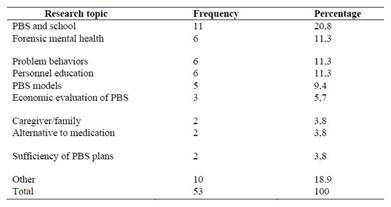
Table 3 shows the distribution of articles on PBS by research topic. 53 articles evaluated within the scope of the research were categorized according to their topic and 9 different categories were created. When the results are examined, it is seen that most of the articles were written on PBS and school with 11 articles. This result was followed by forensic mental health and problem behaviors. Results revealed that articles on PBS focused on different research topics and this shows that PBS as an approach is used by different disciplines.
Distribution of articles on positive behavior support by document type
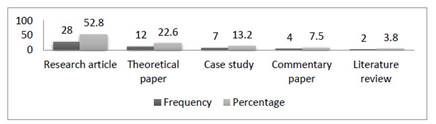
Figure 2 shows the distribution of articles on PBS according to document type. According to the results, there were four different document types used in the articles. The document types included research article, theoretical paper, case study, commentary paper and literature review respectively in terms of their frequency.
Distribution of articles on positive behavior support by research method
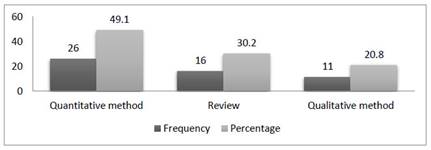
Figure 3 shows the distribution of articles on positive behavior support by research method. According to the results, it was found that the most commonly used method was quantitative method (f=26, 49.1%). This is followed by review (f=16, 30.2%) and qualitative method (f=11, 20.8%).
Distribution of the research methods of the articles on positive behavior support by year of publication
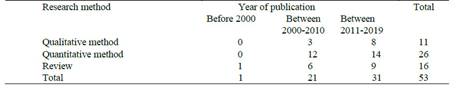
Table 4 presents the distribution of research methods of PBS articles by years. When the table is examined, it is seen that the use of qualitative research method has increased between 2011-2019 compared to the years 2000-2010 when compared to other research methods.
Distribution of articles on positive behavior support by data collection tools
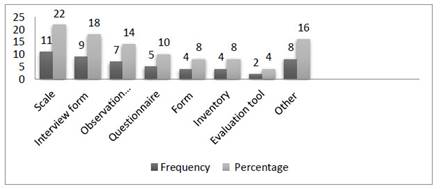
According to the results, two of the 37 research articles were review articles and they were not included in these results since there are no data collection tool. In the remained 35 articles, a single data collection tool was used in 23 articles and more than one data collection tools were used in the 12 articles on PBS. The frequency and percentage values of the results are shown in Figure 4. Results revealed that scale, interview and observation forms were the frequently used data collection tools by researchers working on PBS.
Distribution of articles on positive behavior support by data analysis method
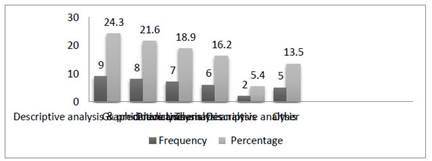
Figure 5 shows the distribution based on data analysis method used in the articles on PBS. When the results are examined, it is seen that descriptive and predictive methods were the most frequently used data analysis methods together. In addition, graphical analysis, predictive analysis, thematic analysis and descriptive analysis were the other frequently used data analysis methods in the articles on PBS.
Distribution of articles on positive behavior support by sample size
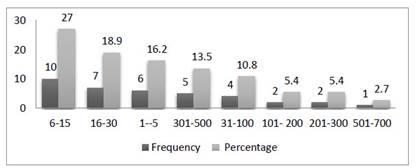
Figure 6 shows the distribution of the articles on PBS according to sample size. When the results are examined, it is observed that the highest rate ranged between 6-15 sample size and 501-700 was the least frequenty studies sample size range.
Distribution of articles on positive behavior support by authors’ field of expertise
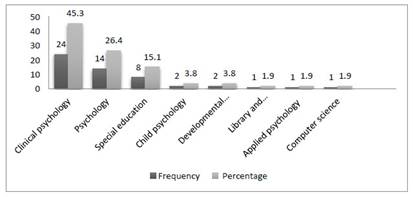
Results on the authors’ field of expertise are shown in Figure 7. According to the results, it was determined that clinical psychology was the most frequent field of expertise of the authors (f=24, 45.3%). This result was followed by psychology (f=14, 26.4%), special education (f=8, 15.1%) and child psychology (f=2, 3.8%). While analyzing the professional fields of the authors, the expertise of the first author was considered as the result for the study and occupational field of the authors was determined based on the last degree of the authors
Discussion
In this study, a total number of 53 articles on positive behavior support published in 35 different scientific journals in Scopus database were examined in order to provide an overview of the studies on PBS through a comprehensive literature review and determine the current trends in the articles on positive behavior support interventions. The articles were examined based on previously determined content analysis criteria including year of publication, country, subject of the journal, research topic, document type, research method, data collection tool, sample size, data analysis method and authors’ field of expertise.
The articles examined in the present study were published between 1998 and 2019 (May). Results showed that the highest number of articles were published between 2011-2019 and the number of articles published on this subject increased from the past to the present. This suggests that PBS has gained importance in the recent years. In parallel with these results, Tanhan and Cevik (2018) emphasized the increasing prevalence of positive behavior support especially in school environments for reducing or preventing problem behaviors and creating positive school environments. In the study, it was also determined that PBS was mostly studied by researchers in the United Kingdom and USA in the recent years. Therefore, it could be inferred that PBS as an approach is mostly referred in professional and educational literature of these two countries.
When the distribution of the subjects of the journals in which the articles on PBS were published is examined, it is seen that majority of the articles were published in Tizard Learning Disability Review. The subject categories of the journals were found as learning disability, developmental delay, emotional / behavioral problems, forensic psychiatry / psychology, mental health, school psychology, educational studies and children / family. In this study, it was also determined that "PBS and school" was the most frequently discussed research topic. This might be related with the increasing evidence for the positive outcomes of PBS interventions in school environments (Freeman et al., 2016; Hieneman & Fefer, 2017; Gage et al., 2019).
Results indicated that most of the published documents on PBS were research articles. According to this result, it can be inferred that authors prefer to publish research articles when compared to other document types. In addition, theoretical paper, case study, commentary paper and literature review were also found as the other document types used by researchers. This result is parallel with the results of other researches which analyzed the research articles on PBS (Horner, Sugai & Anderson, 2010; Solomon et al., 2012). Furthermore, it was determined that the most frequently used research method was quantitative method, followed by review and qualitative research respectively and the use of qualitative research method has increased between 2011-2019 compared to the years 2000-2010 when compared to other research methods.
It was observed that the scales were the most commonly used data collection tools in the articles on PBS. This might be related with the fact that scales provide low-cost and validated data in a short period of time and examine certain events, phenomena and objects in terms of scientific research (Bayat, 2014). When the findings related to sample size are examined, it is seen that the highest rate ranged between 6-15 sample size. It was also found that descriptive and predictive analysis methods were used together as the data analysis method, followed by graphical analysis, predictive analysis, thematic analysis and descriptive analysis methods. The reason why quantitative data analysis methods are frequently used is that the features examined among variables can be explained and interpreted more easily (Bektas & Ceylan, 2013; Gunay & Aydin, 2015).
It was determined that the most common professional fields of the authors were clinical psychology, followed by psychology, special education, child psychology and developmental psychology, library and knowledge management, applied psychology and computer science. According to these results, it is remarkable that researchers concentrated on PBS are generally from the fields of psychology. This might be entirely related with the notion that the origins of PBS come from applied behavior analysis and psychology (Johnston et al., 2006). However, it is also noteworthy that PBS approach is open to multidisciplinary practice and there is a need for this approach to be adequately introduced for other professional fields. It is considered that researches to be carried out by other professionals will add richness to the field and will support the further development of this approach.
Conclusion and Recommendations
The results of this study focusing on articles related with PBS are limited to a total of 53 articles published in 35 different scientific journals in Scopus database between 1998-2019 (May). It is considered that result obtained from the present study can be used as an important source in terms of giving an idea about the current situation and trends in research on PBS and guiding further research. Accordingly, it is expected that further research with the inclusion of more databases will provide more generalizable information on this subject. In line with the results, recommendations for further research and practices are as follows:
The application of a multidisciplinary practice such as PBS by professionals from different fields such as psychiatry, nursing and social work may lead to a more widespread use of PBS.
Other scientific databases might be examined in order to reveal the trends in research on PBS.
Guidelines for how to apply PBS approach in practical settings should be prepared in order to extend the use of PBS accross different settings such as general and special education environments.
This study might be replicated periodically in order to determine current trends on PBS research and reveal the progress throughout the years