Services on Demand
Journal
Article
Indicators
-
 Cited by SciELO
Cited by SciELO
Related links
-
 Similars in
SciELO
Similars in
SciELO
Share
Revista de la Facultad de Medicina Humana
Print version ISSN 1814-5469On-line version ISSN 2308-0531
Rev. Fac. Med. Hum. vol.21 no.1 Lima Jan-Mar 2021
http://dx.doi.org/10.25176/rfmh.v21i1.3437
Original article
Hypoalbuminemia and mortality of sepsis from covid-19 in a Hospital in Chocope, Perú,2020
1Universidad César Vallejo, Trujillo-Perú.
Introduction:
A correlational type investigation was carried out evaluating 145 patients with COVID-19 sepsis.
Objectives:
To determine whether hypoalbuminemia is a predictor of mortality and to identify the serum albumin value most frequently related to lethality.
Method:
Patients older than or equal to 18 years seen at Hospital II Chocope during May to August 2020 were included. Patients with oncological pathologies and incomplete medical records were excluded. The documentary analysis technique was used, by reviewing medical records.
Results:
There was a statistically significant association between hypoalbuminemia and mortality (p=0.014), patients with hypoalbuminemia had 3 times the risk of dying. (OR=3.97 95% CI of 1,24-12,74). Likewise, the highest sensitivity and specificity of the test was when the cut-off point for hypoalbuminemia was 1.38 g / dl. Finally, the most frequent comorbidity was arterial hypertension.
Conclusions:
Hypoalbuminemia can be a predictor of mortality in patients with sepsis due to COVID-19 at the Hospital de Chocope because it has a statistically significant association, with three times the risk of death. The highest sensitivity and specificity was obtained with an albuminemia cutoff of 1.38 g / dL. The most frequent comorbidity in patients with sepsis due to COVID-19 who died was arterial hypertension.
Key words: Hypoalbuminemia; Mortality; Sepsis; COVID-19. (Source: MeSH NLM)
INTRODUCTION
Sepsis is the main cause of death in hospitalized critically ill patients with a high mortality rate.1,2Each year in the United States, 751,000 cases of sepsis are reported with an approximate mortality of 26.6% and an annual cost of 16.7 billion dollars, increasing by 9% each year.3Likewise, the incidence of sepsis is also high in our country.4Despite advances in diagnostic methods and therapeutic management, sepsis continues to be a challenge for different doctors in our country.
Likewise, currently, cases of sepsis have increased with COVID-19 as the main causal agent. This being a highly contagious virus. Since the first case was discovered in December 2019 in Wuhan, the COVID-19 infection has spread rapidly. Until March 5, 2020, around 86 countries, including six in Latin America, had reported at least one laboratory-confirmed case of COVID-19, which is why the COVID-19 outbreak was declared a pandemic, reaching our territory on March 6, 2020.5
Currently, there are countries that are known to have had a high mortality rate. For example, in March, Spain presented a high rate of infected with 1,549 cases/million inhabitants, adding around 72,248 cases, continuing with Italy where 1,529 cases / million inhabitants are reported with a total sum of 92 472 cases and France with 493 cases / million inhabitants, with a total of 39,964 cases.6
In Peru, the case curve is increasing. The group of older adults have the highest mortality rate; considering that the departments with the highest deaths from COVID-19 are Ancash, Callao, Ica, La Libertad, Lambayeque, Lima, and Piura7. Hypoalbuminemia being a frequent condition in older adults, it is considered important to establish whether hypoalbuminemia is a predictor of mortality. Therefore, the objective of the study was to determine whether hypoalbuminemia is a predictor of mortality in patients with sepsis due to COVID-19 hospitalized in the clinical service of Hospital II Chocope in 2020 and to identify the serum albumin value most frequently related to lethality.
METHODS
Design and study area
A retrospective survey was conducted in patients diagnosed with COVID-19 sepsis in the Hospital II Chocope medical service from May to August 2020.
Population and sample
208 patients diagnosed with COVID-19 sepsis hospitalized in the medical service of Hospital II Chocope from May to August 2020 were considered. We worked with the total population for which the sample will have a census character. The unit of analysis was each of the patients with covid-19 sepsis mentioned in the population using their medical records. Patients aged 18 years or older with a diagnosis of COVID-19 sepsis were included based on the diagnosis given in the clinical record. Also, the following were considered as exclusion criteria: pathologies also associated with hypoalbuminemia and incomplete medical records (63 stories).
Variables and instruments
The documentary analysis technique was used, by reviewing the medical records that contained the complete information required for the study. As well, the instrument used was validated by the criteria of 3 judges, made up of 3 internal medicine specialists, who gave their approval to the instrument. Hypoalbuminemia was measured as follows: mild was considered to be between 3.5 g/dL to 3 g/dL, moderate between 3 to 2.5 g/dL and severe when less than 2.5 g/dL.
Procedures
Permission was obtained from the II Chocope hospital director to access the file and proceed with the collection of data from patients diagnosed with sepsis by covid-19 during May to August 2020. This information was filled in a collection form for subsequent analysis in Excel.
Statistical analysis
The data were subjected to descriptive statistical analysis using percentages, averages and the interpretation of tables and graphs. Statistical significant relationship and odds ratio were determined to assess the risk of death. Likewise, the SPSS version 25 statistical software was used to perform the ROC curve to find the best cutoff point for predicting mortality.
Ethical aspects
Regarding ethical aspects, it had the permission of Hospital II de Chocope, it also complies with article 42 of the Code of Ethics of the Medical College of Peru and also complies with principle number 6 of the Declaration of Helsinki, in the 64th assembly held in Strength.8
Since it is a retrospective study using medical records, it was not necessary to request informed consent. It ensures the confidentiality of the data provided.9
RESULTS
Table 1. Hypoalbuminemia and mortality in patients with sepsis due to COVID - 19 hospitalized in the medical service of hospital II Chocope
| Hypoalbuminemia | Mortality | Total | ||||
| Yes | No | |||||
| n | % | n | % | N | % | |
| Yes | 67 | 94,4% | 59 | 80,8% | 126 | 87,5% |
| No | 4 | 5,6% | 14 | 19,2% | 18 | 12,5% |
| Total | 71 | 100,0% | 73 | 100,0% | 144 | 100,0% |
| Odds ratio = 3.97 I.C. al 95% ( 1.24; 12.74 )X 2= 6.04 p = 0.014 * | ||||||
In this table we observe that 94.4% of the patients who died presented hypoalbuminemia; while in the group of patients who did not die, hypoalbuminemia appeared in 80.8%. It was determined that there is a statistically significant association between hypoalbuminemia and patient mortality (p = 0.014). Also, a 3.97 times greater risk of death was identified when presenting hypoalbuminemia in relation to the group of patients who presented normal albumin (OR = 3.97 95% CI 1.24 to 12.74). On the other hand, the mean albumin values for the patients who died were 2.38 g / dl (± 0.67) vs. at 3.02 g / dl (± 0.65) for the other group.
Table 2. Serum albumin levels and lethality in patients with sepsis due to COVID - 19 hospitalized in the Medical service Hospital II Chocope, 2020.
| Serum albumin level | Mortality | Total | ||||
| Yes | No | |||||
| n | % | n | % | n | % | |
| Normal | 4 | 2,8% | 14 | 9,7% | 18 | 12,5% |
| Mild | 5 | 3,5% | 38 | 26,4% | 43 | 29,9% |
| Moderate | 26 | 18,1% | 10 | 6,9% | 36 | 25,0% |
| Severe | 36 | 25,0% | 11 | 7,6% | 47 | 32,6% |
| Total | 71 | 49,3% | 73 | 50,7% | 144 | 100,0% |
| X 2= 51.27 g.l. = 3 p = 0.000** | ||||||
This table shows the highly significant relationship between serum albumin levels and mortality (p = 0.00 <0.01) in patients with covid-19 sepsis. Also, 25 % of the patients had a severe albumin level and died while 26.4% of patients had mild hypoalbuminemia, and no deaths were recorded in this group.
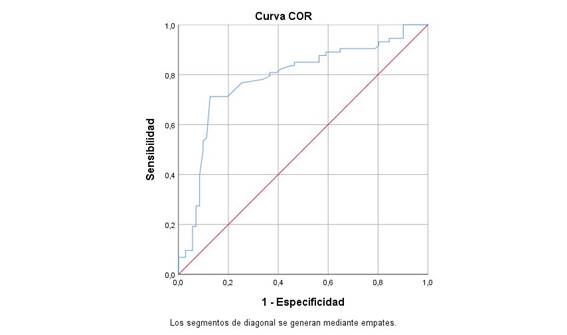
Graph 1. CROC curve of hypoalbuminemia in relation to mortality in patients with sepsis due to COVID-19 hospitalized in the Medical service Hospital II Chocope 2020
The area under the curve indicates that the cut-off point for hypoalbuminemia is 1.38, which determines the highest sensitivity and specificity of the test.
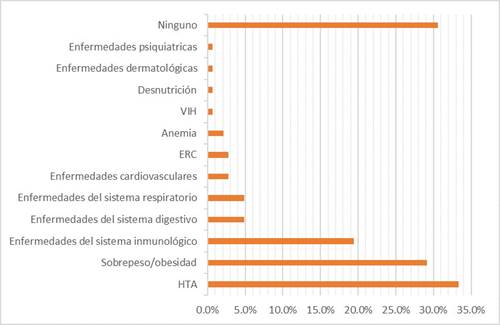
Graph 2. Comorbidity in patients with sepsis due to COVID - 19 hospitalized in the Medical service Hospital II Chocope, 2020
In this graph, it can be seen that the most frequent comorbidity in patients with covid sepsis was arterial hypertension, represented by 33.3%, and in second place, both overweight and obesity (29.2%). Likewise, 30.6% of patients did not present any comorbidity.
DISCUSSION
Although our finding of hypoalbuminemia as a predictor of mortality is not new, and numerous studies reported that hypoalbuminemia was associated with increased mortality in different patient groups and settings. It considers itself a poor prognostic factor in inflammatory processes8-14. This is one of the first studies that evaluate hypoalbuminemia in patients with sepsis due to covid-19. Due to the current contingency, it was necessary to have enough tools to predict and prevent mortality.
Albumin levels can decrease due to several factors including poor nutritional status. Also, inflammation (eg, infectious disease, malignancy), due to interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor that decrease albumin production by the liver. Kidney disease or burns, due to loss of albumin in the urine or integument, respectively. Trauma or surgery results from associated stress, which increases protein and energy requirements by creating a hypermetabolic, catabolic state. Finally, liver disease.15Hypoalbuminemia patients may manage critical illness somewhat differently than patients with normal or high albumin levels.
Hypoalbuminemia in severe patients is related to an increased pro-inflammatory response to various infections. Both the severity of the disease and hypoalbuminemia are closely related in adult and pediatric patients.10,14
Our results indicate an association between low levels of albumin and increased mortality; the lower the albumin level, the more frequent mortality was evident in all age groups. This relates to the results obtained by Luna J , et al16, whose albumin values less than 3.5 g / dl within the first 2 days of admission showed a high risk of death with an OR 1.5 higher, especially in patients with albumin levels between 2.4-1.6 g / dl.
Cerpa et al.17analyzed 35 patients, with the mean serum albumin of 2.84 g / dl in the group of patients with mortality and obtained a Chi 2 = 8.67 with a significance level of p-value = 0.05, in addition all the deceased patients presented hypoalbuminemia almost similar to our study (94.4%).
Villalba S, et al.18found that among the factors associated with high mortality is arterial hypertension (p = 0.025), the same one that represents the 33.3% of associated comorbidities in our study. Likewise, Jellinge et al.19found that hypoalbuminemia’s discriminatory capacity was good (AUROC 0.73 (95% CI, 0.70-0.77)) and the calibration was acceptable, similar to what our study obtained. study.
Our study focused on analyzing the albumin values generally obtained in the first 24 hours of sepsis patients due to covid-19 admitted to the Medical service. The results indicate high mortality in patients with decreased albumin values and the population at risk were adults with a predominance of older adults and men. For this reason, we believe that serum albumin control is important in all patients who need hospitalization for COVID 19.
Since the study was based on a review of medical records, some data such as nutritional status and body mass index did not register. Another limitation was the lack of data on the specific cause of mortality, and no information was available on the intravenous administration of albumin during hospitalization.
CONCLUSION
Hypoalbuminemia is a predictor of mortality in patients with covid sepsis at the Hospital de Chocope because it is highly significant, with 3 times higher risk of dying. The highest sensitivity and specificity of the test was when the cut-off point for hypoalbuminemia was at 1.38 g / dl. The most frequent comorbidity in patients with COVID-19 sepsis who died was arterial hypertension.
REFERENCES
1. Seymour C, Vincent L, Iwashyna T, Brunkhorst F, Rea T, Scherag A, et al. Assessment of clinical criteria for sepsis: for the Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA (Internet) 2016 Febrero (Consultado el 16 de julio del 2020);315(8):801-10. Disponible en: https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2492875 [ Links ]
2. Neira-Sánchez E, Málaga G. Sepsis-3 y las nuevas definiciones, ¿es tiempo de abandonar SIRS? Acta Med Perú. (Internet) 2016 Marzo (Consultado el 16 de julio del 2020);33(3):217-22. Disponible en: http://www.scielo.org.pe/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1728-59172016000300008 [ Links ]
3. Carrillo R, Carrillo J, Carrillo L. Estudio epidemiológico de la sepsis en unidades de terapia intensiva mexicanas. Revista Cir Cir. (Internet) 2009 Julio (Consultado el 17 de julio del 2020); 77:301-308. Disponible en: https://www.redalyc.org/pdf/662/66211210008.pdf [ Links ]
4. Liñán-Ponce J, Véliz-Vilcapoma F. Características clínicas de los pacientes con sepsis severa admitidos a una Unidad de Cuidados Intensivos. Rev Soc Perú Med Interna. (Internet) 2008 Marzo (Consultado el 18 de julio del 2020); 21 (4).139. Disponible en: http://www.medicinainterna.org.pe/revista/revista_21_4_2008/03.pdf [ Links ]
5. Mejía F, Medina C, Cornejo E, Morello E, Vásquez S, Alave J, et al. Características clínicas y factores asociados a mortalidad en pacientes adultos hospitalizados por COVID-19 en un hospital público de Lima, Perú. Rev. Perú. Med. Exp. salud publica (Internet) 2020 Julio (Consultado el 18 de agosto del 2020); 37 (2). Disponible en: 858-Preprint Text-1244-3-10-20200628.pdf [ Links ]
6. Cavarelli A, Irisarri M, Bittar G, Cuello G, Perez M, Aleman A, Modelos epidemiológicos en la pandemia por SARS-CoV-2: concepto, aplicaciones y alcance. Rev. urug. med. interna. Junio 2020 ;5(2):4-8. [ Links ]
7. Asociación Médica Mundial. Principios éticos para las investigaciones médicas en seres humanos. (Internet) 2017 Octubre (Consultado el 1 setiembre del 2020) Disponible en: https://www.wma.net/es/policies-post/declaracion-de-helsinki-de-la-amm-principios-eticos-para-las-investigaciones-medicas-en-seres-humanos. [ Links ]
8. Colegio Medico Del Perú. Código de Ética y Deontología del Perú. (Internet) 2008 (Consultado el 1 setiembre del 2020); Capítulo 6 del Trabajo de Investigación. Articulo 42. Disponible en: https://www.cmp.org.pe/wp-content/uploads/2020/01/CODIGO-DE-ETICA-Y-DEONTOLOG%C3%8DA.pdf. [ Links ]
9. Ministerio de Salud de Peru Centro Nacional de Epidemiologia Prevencion y Control de Enfermedades. Situación Actual "COVID-19" Perú - 2020. Informe N° 31. [ Links ]
10. 10. Hernández Rodríguez José. Clinical aspects related to the Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS-CoV-2). Rev haban cienc méd (Internet). 2020 (citado 2020 Oct 06);19 (Suppl 1): e3279. Disponible en: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1729-519X2020000400003&lng=es. Epub 01-Jun-2020 [ Links ]
11. Trujillo Ramírez Nancy, López Reséndiz Sergio Michel, Méndez Reyes Raquel, Villagómez Ortiz Asisclo de Jesús, Rosas Barrientos José Vicente. Índice lactato/albúmina como predictor de mortalidad en sepsis y choque séptico. Med. crít. (Col. Mex. Med. Crít.) (revista en la Internet). 2018 Jun (citado 2020 Oct 06) ; 32( 3 ): 136-140. Disponible en: http://www.scielo.org.mx/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S2448-89092018000300136&lng=es. Epub 27-Mar-2020. [ Links ]
12. Godínez A, Correa A, Enríquez D, Pérez S, López S, Gracida N ¿Es la albúmina un predictor de gravedad y de mortalidad en pacientes con sepsis abdominal? Revista Cir Cir. (Internet) 2019 Mayo (Consultado el 18 de julio del 2020); 87:485-489. Disponible en: https://www.medigraphic.com/pdfs/circir/cc-2019/cc195a.pdf [ Links ]
13. Torres G. Eficacia de los niveles de albúmina como marcador de mortalidad en pacientes sépticos en el hospital Teodoro Maldonado Carbo del 1 de enero al 31 de diciembre de 2017. (Tesis) Guayaquil Universidad Católica de Santiago de Guayaquil; 2018 (Consultado el 19 julio 2020) Disponible en: https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/9d89/b24de51e0c550be3ad2da655d3028a8030e9.pdf [ Links ]
14. Akirov A, Masri-Iraqi H, Atamna A, Shimon L. Low Albumin Levels Are Associated with Mortality Risk in Hospitalized Patients. The American Journal of Medicine (Internet) 2017 Diciembre (Consultado el 18 de setiembre del 2020); 130 (12). Disponible en: .https://www.amjmed.com/article/S0002-9343(17)30800-8/pdf#:~:text=Compared%20with%20patients%20with%20normal%20albumin%20levels%2C%20marked%20hypoalbuminemia%20was,3.4%20(3.3%2D3.5) [ Links ]
15. Valenzuela-Landaeta K., Rojas P., Basfi-fer K.. Evaluación nutricional del paciente con cáncer. Nutr. Hosp. (Internet). 2012 Abr (citado 2021 Ene 13); 27( 2 ): 516-523. Disponible en: http://scielo.isciii.es/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0212-16112012000200025&lng=es [ Links ]
16. Luna J. Hipoalbuminemia como factor predictivo de mal pronóstico en sepsis neonatal en la UCIN del Hospital Dr. Francisco De Icaza Bustamante periodo Marzo a Septiembre 2019 (Tesis) Universidad Católica De Santiago De Guayaquil ;2020 (Consultado el 13 Octubre 2020) Disponible en: http://repositorio.ucsg.edu.ec/bitstream/3317/14225/1/T-UCSG-POS-EN-3.pdf. [ Links ]
17. Cerpa E. Niveles de albumina y presion arterial como predictor de mortalidad en pacientes con insuficiencia renal cronica terminal, Hospital Carlos Monge Medrano Juliaca en el 2017 (Tesis) Universidad Nacional del Altiplano; 2017 (Consultado el 13 Octubre 2020) Disponible en: http://repositorio.unap.edu.pe/handle/UNAP/6448. [ Links ]
18. Villalba S, Alfonso A, Acuña J, Sawatzky D, Albúmina y PCR como predictores de mortalidad en pacientes con pancreatitis aguda. Revista Discov. med (Internet) 2018 Julio (Consultado el 13 de Octubre del 2020); 2(1):11-20.. Disponible en: https://www.revdiscovermedicine.com/index.php/inicio/article/view/80. [ Links ]
19. Jellinge M, Henriksen D, Hallas P, Brabrand M. Hypoalbuminemia is a strong predictor of 30-day all-cause mortality in acutely admitted medical patients: a prospective, observational, cohort stud. PLoS One. (Internet) 2014 Agosto (Consultado el 30 de setiembre del 2020); 9 (8). Disponible en: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0105983. [ Links ]
Received: December 01, 2020; Accepted: January 06, 2021











 text in
text in 


